"He who loves practice without theory is like the sailor who boards ship without a
rudder and compass and never knows where he may cast"
LEONARDO DA VINCI - Thoughts
Introduction
The terms 'diagnostics' and 'monitoring' refer to the process of understanding the state of conservation of a building, identifying the problems (particularly their seriousness and urgency in terms of safety), and verifying the subsequent effectiveness of the interventions put in place. This last step is performed through measurements of significant parameters (amplitude cracks, subsidence, temperature, etc.) at specific time intervals.
Diagnosis
The main diagnosis of materials consists of:
- direct observation or macroscopic analysis.
- precision observation, through in situ microscopic analysis or by sampling in the laboratory
It's vital to uncover historical information about the site, such as changes to the original building, then move on to the geometries, materials, cracks, and degradation. This allows you to draw up an investigation project and to execute it. An investigation project ends with post-intervention monitoring, useful for understanding the effectiveness of the consolidation in place. Our work deals mainly with problems related to structure, intervening from the first phase up to the drafting of the investigation plan. We rely on university laboratories, such as the Pietro Pisa laboratory at the University of Brescia or the Laboratory of Diagnostics and Investigations of Building Materials at the Milan Polytechnic, as well as companies specialized in on-site and laboratory material tests. We perform the post-intervention monitoring phase jointly.
Historical overview
Research consists of consulting archives, paper documents, images, or period photographs that allow us to reconstruct a set of historical circumstances. This helps to define and describe the facts that led to the of situation in question.
Geometric and material relief
When we speak of geometric relief, we mean the set of operations used to find out information about the structure. This information is then transferred to a paper or electronic format for subsequent reprocessing, for a study, or for a possible new project.
Relief can be either manual or instrumental, and can concern the characteristics of a structure (geometric) or of a terrain or a road (topographic). The survey can also be performed with laser-scanner.
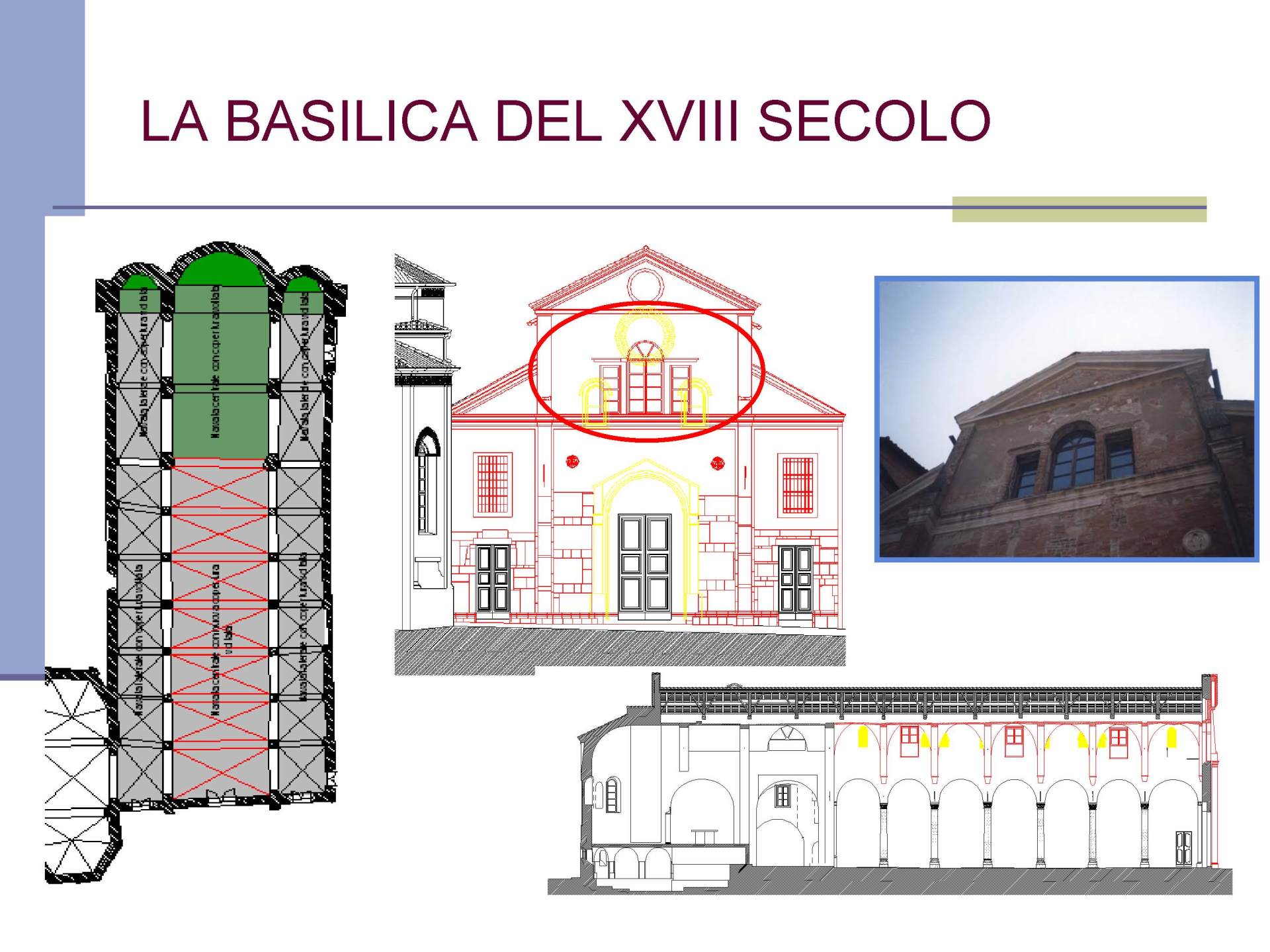
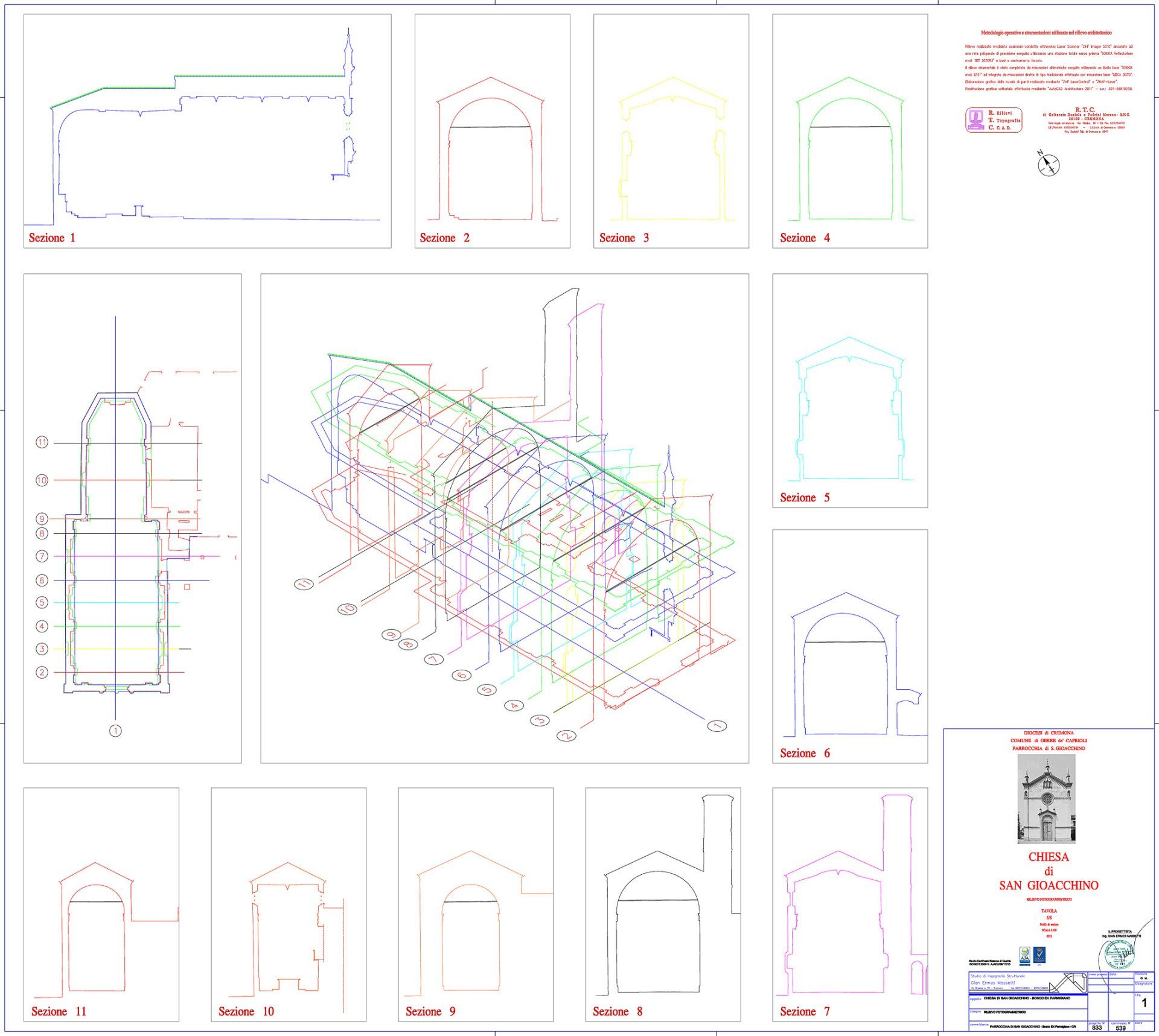
Church of San Gioacchino - Bosco ex Parmigiano
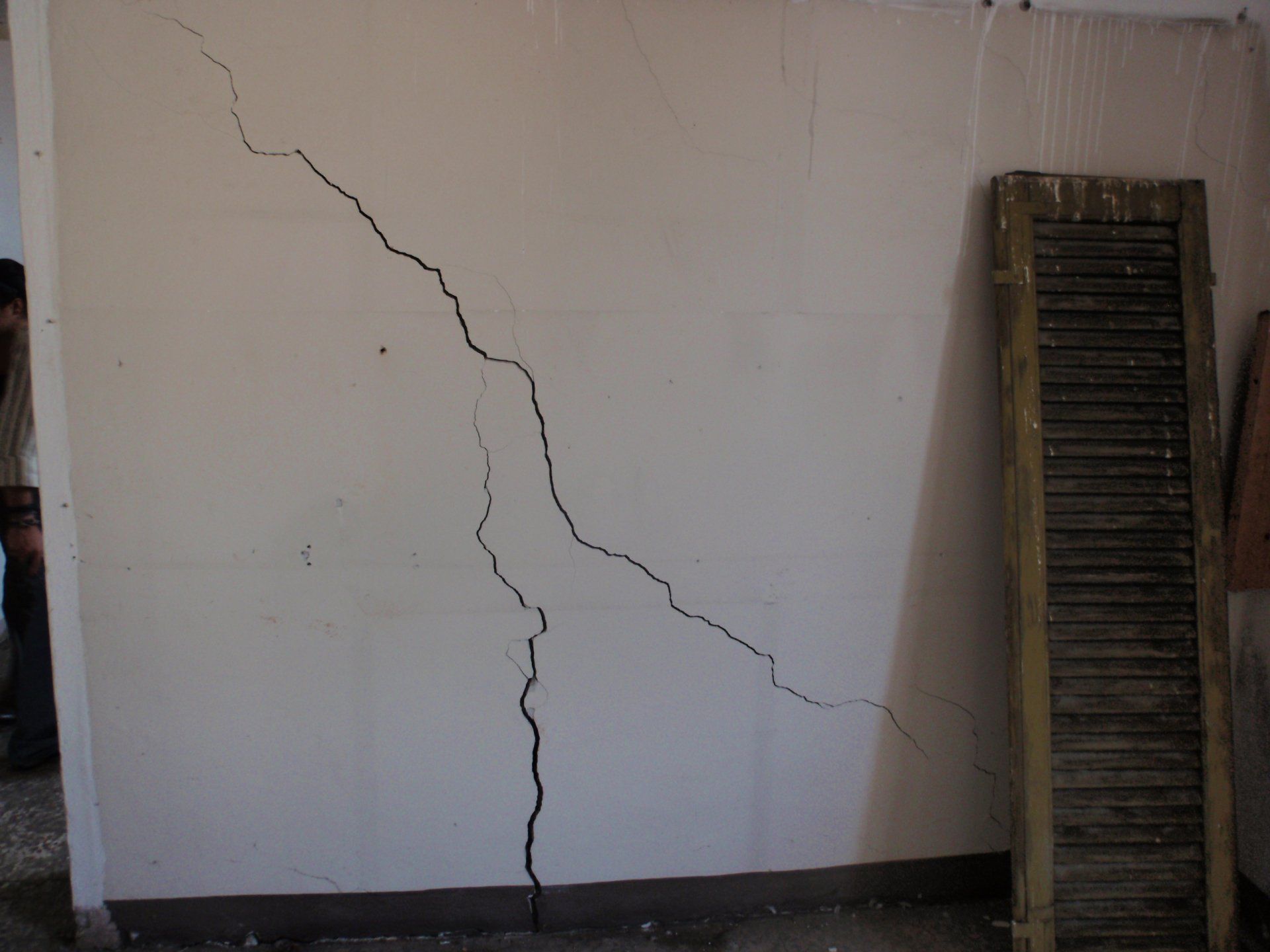
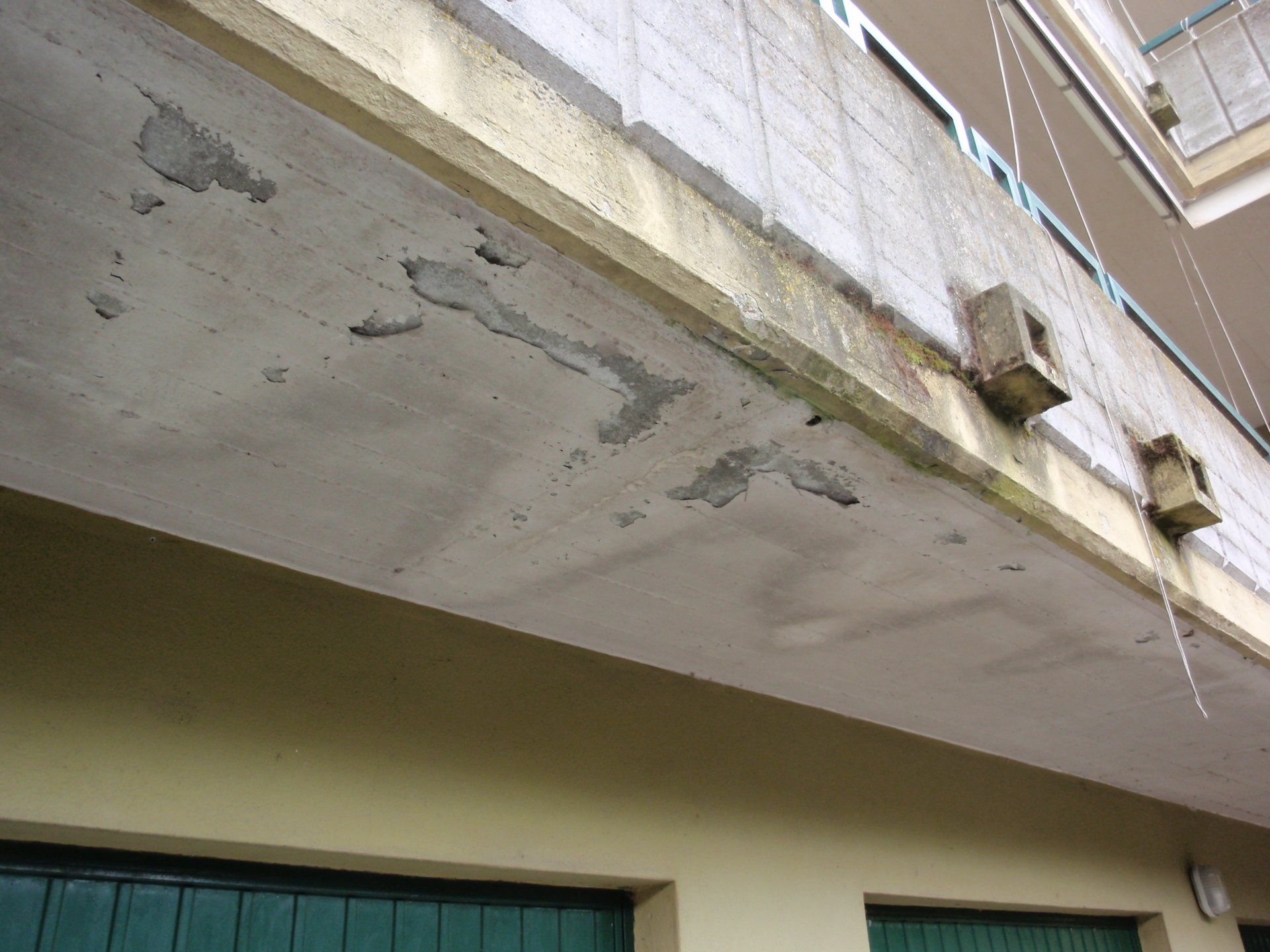
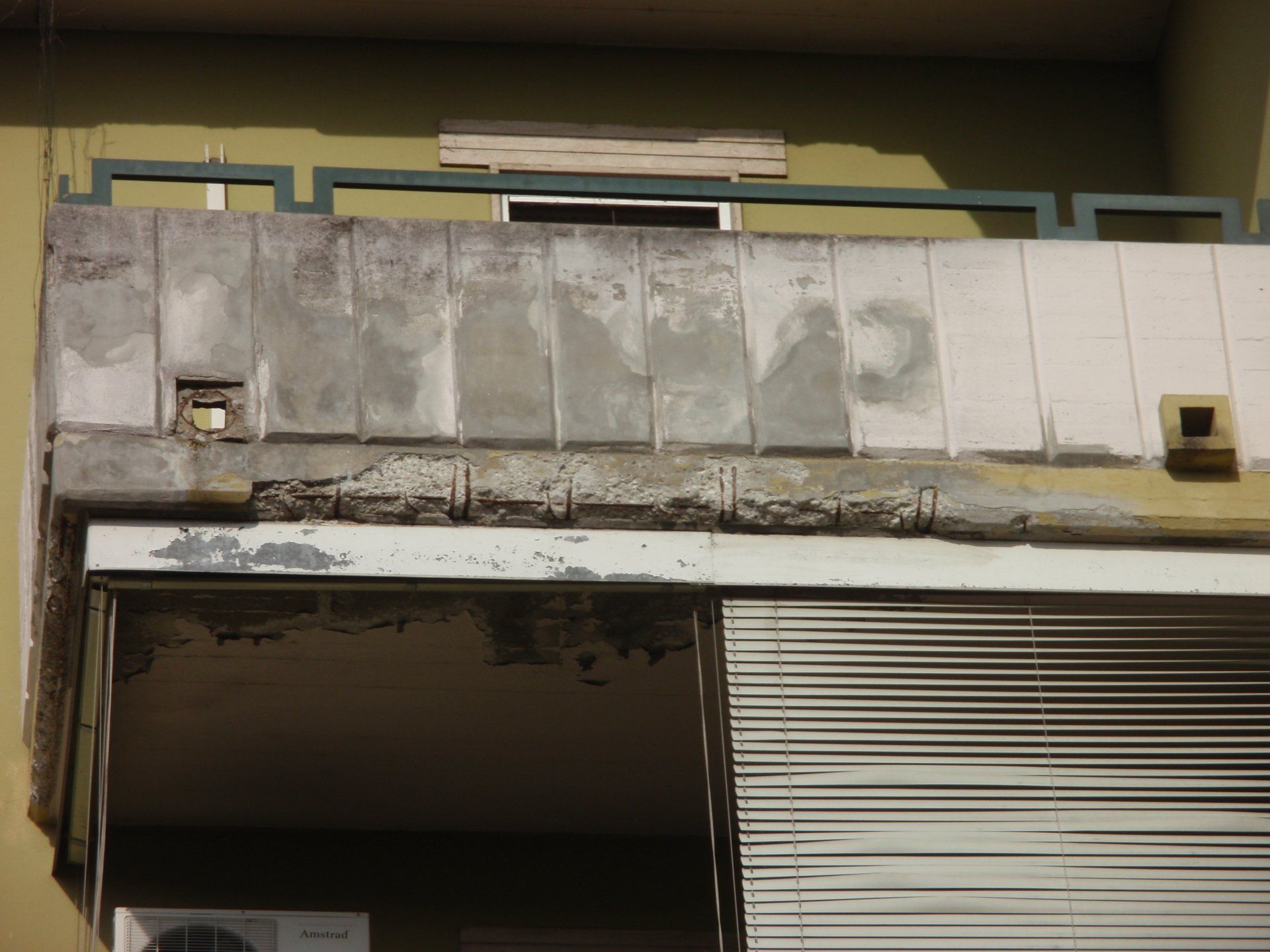
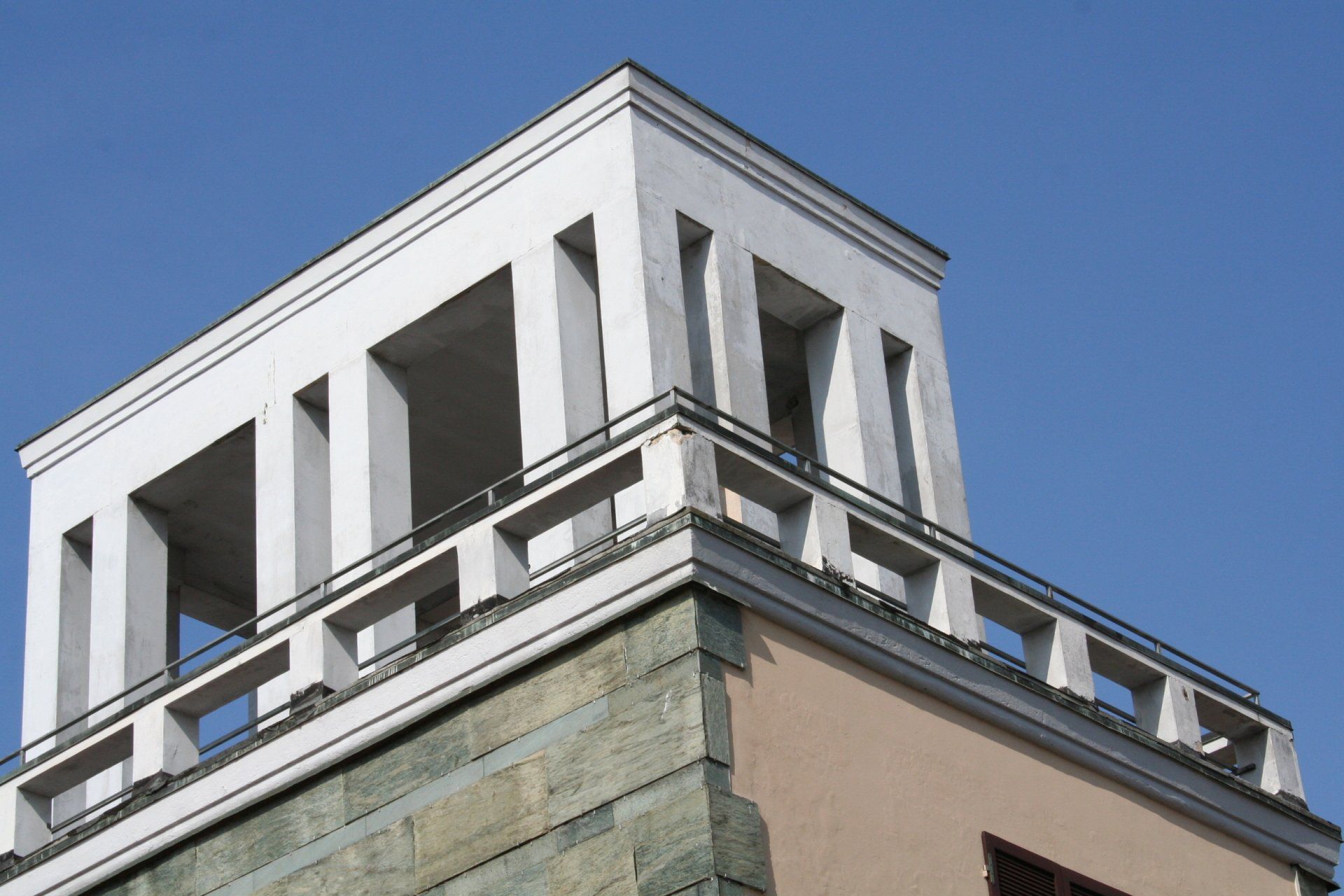
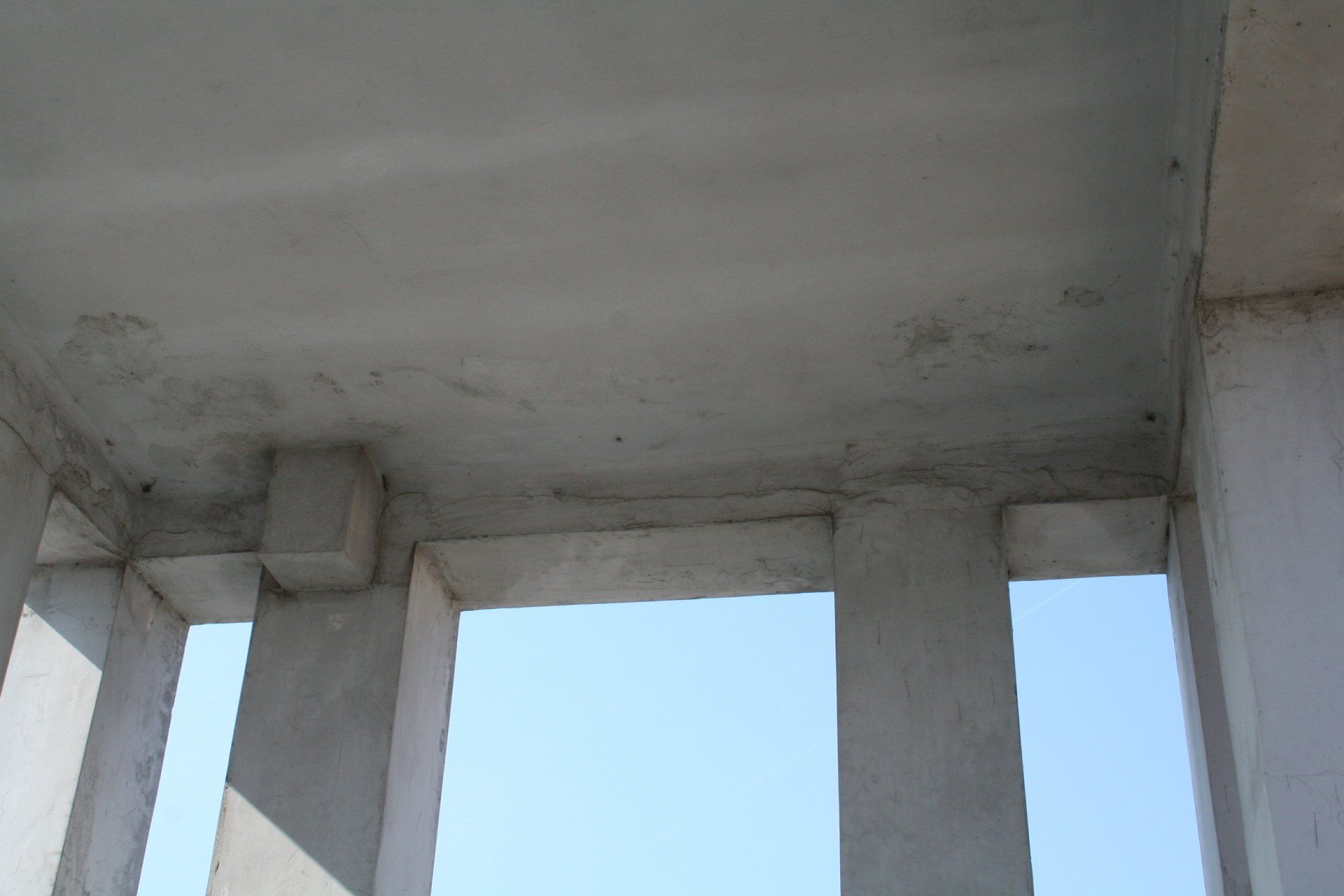
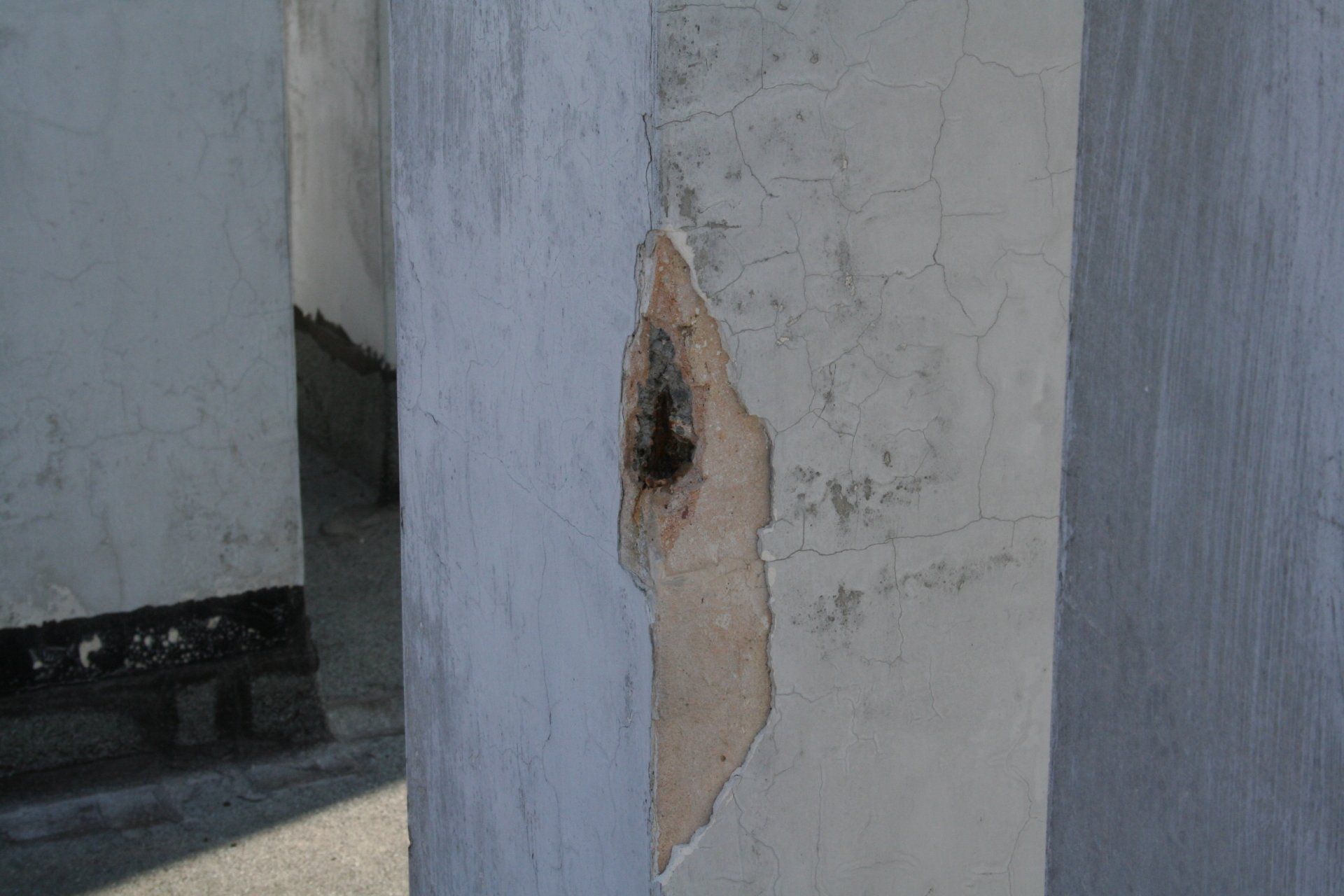
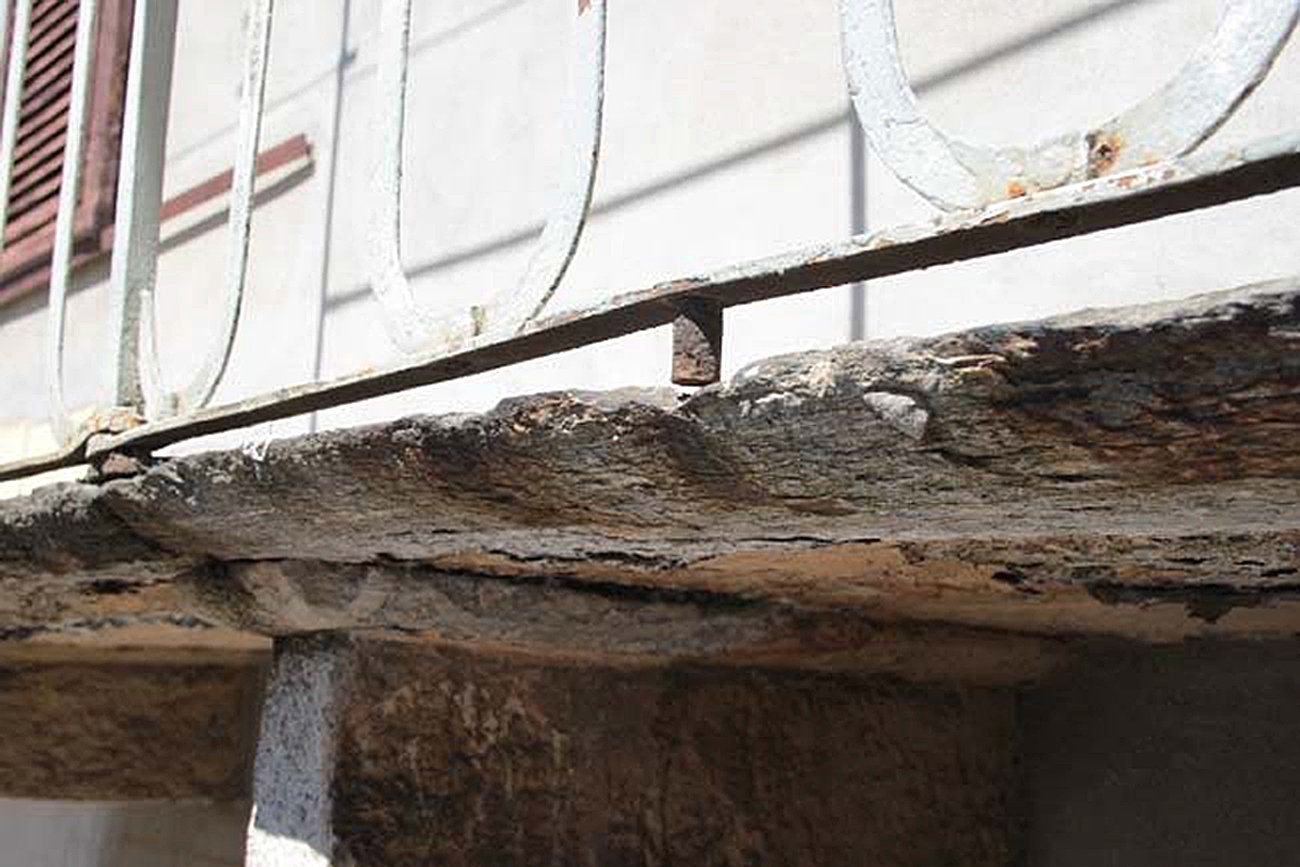
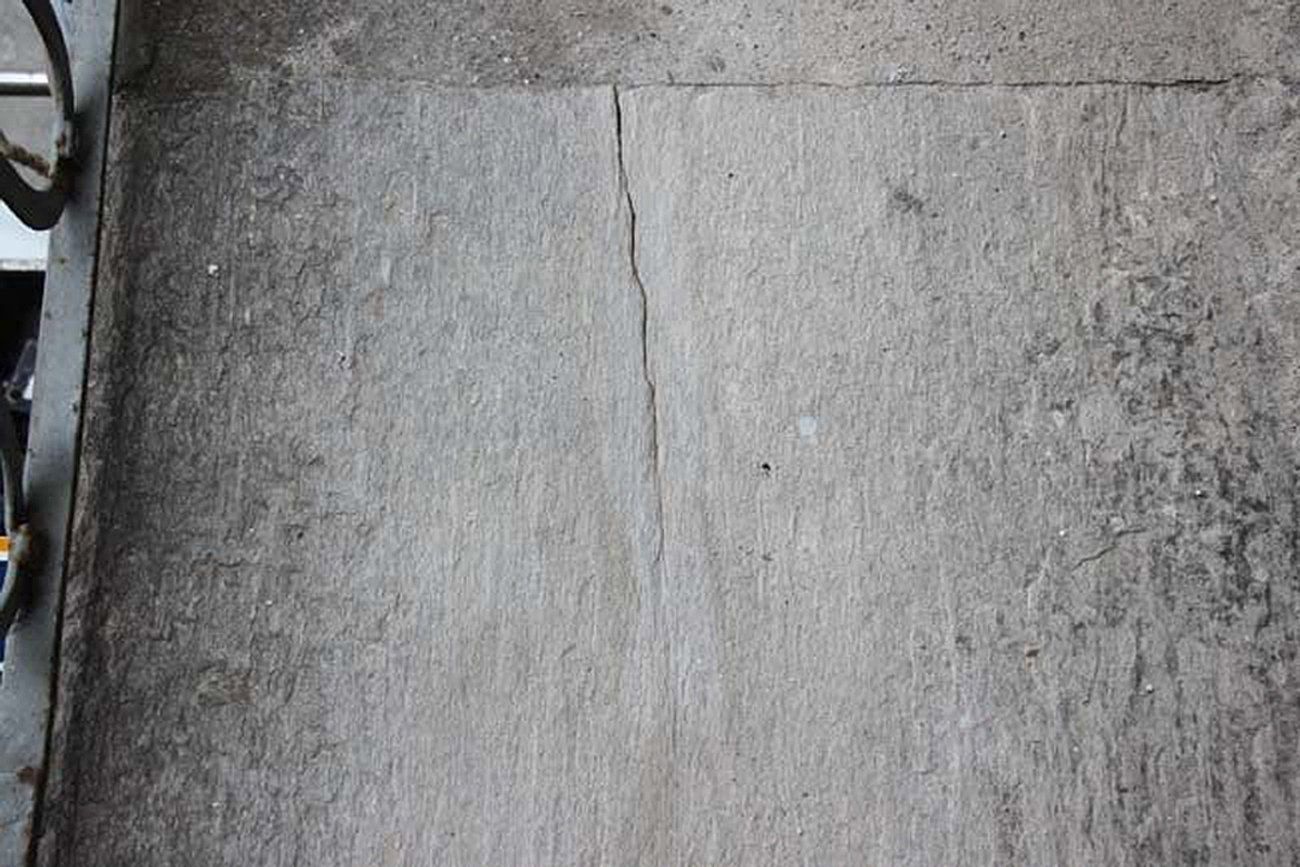
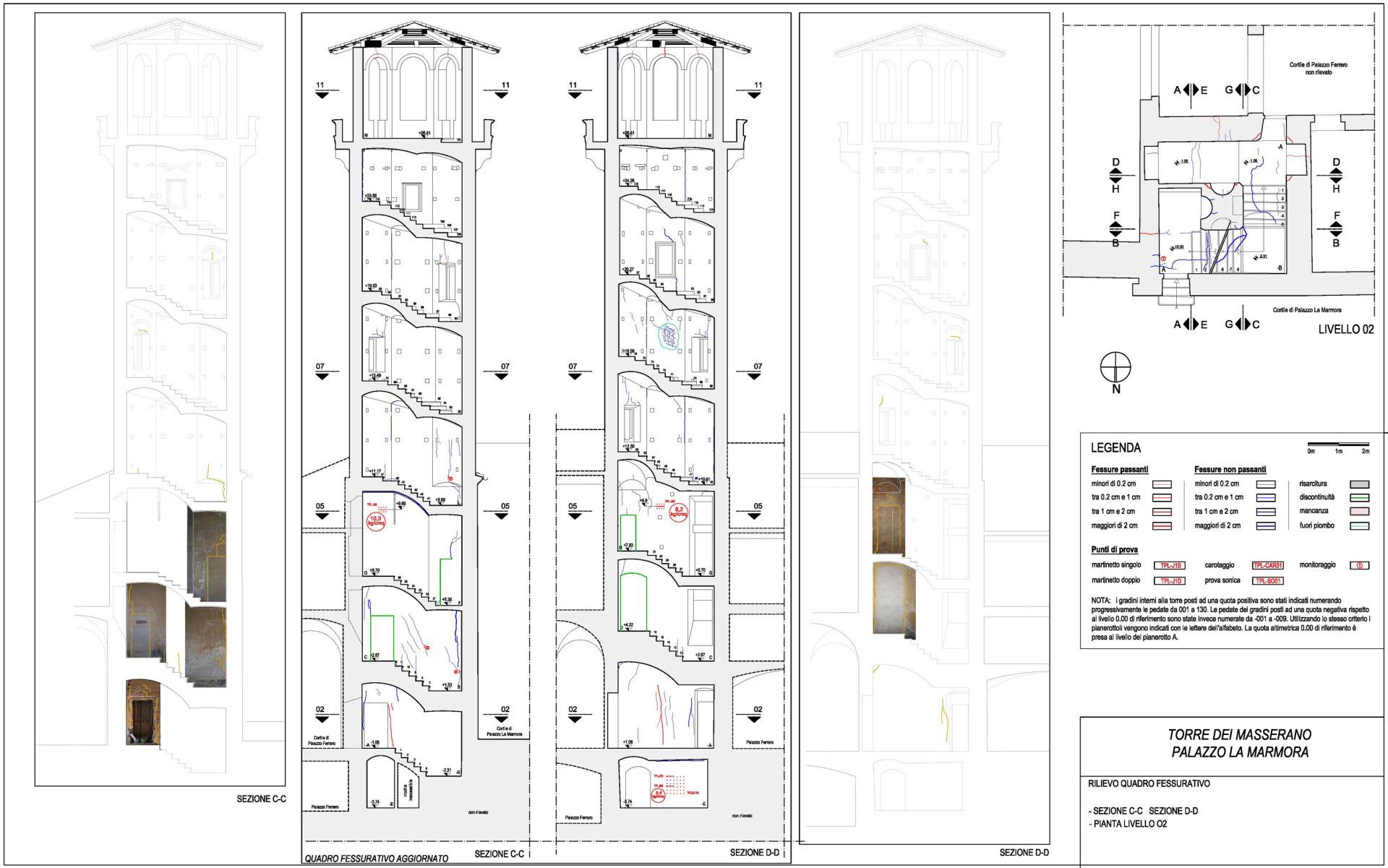
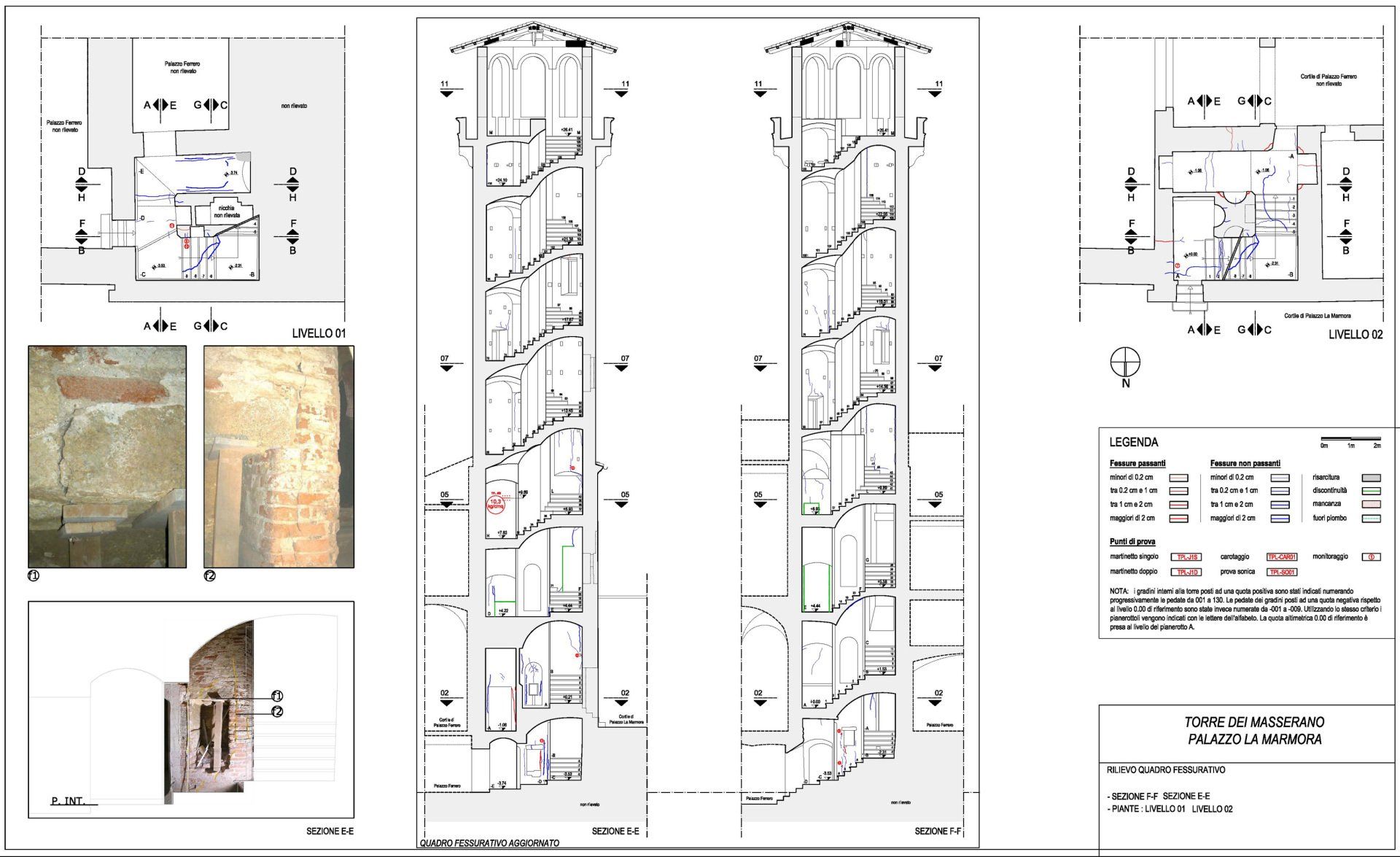
Cracks and the state of degradation
Visible or not, lesions and cracks form on structural elements due to a failure in design or chemical, physical, or biological degradation.
The term 'deterioration' refers to the situation in which the building is found at the time of the survey. This represents the state of neglect and the current damage, caused by various factors such as weathering, age, abandonment, or neglect.
The crack pattern and the state of degradation go hand in hand and often cause one another.
QF Palazzo La Marmorma - Biella
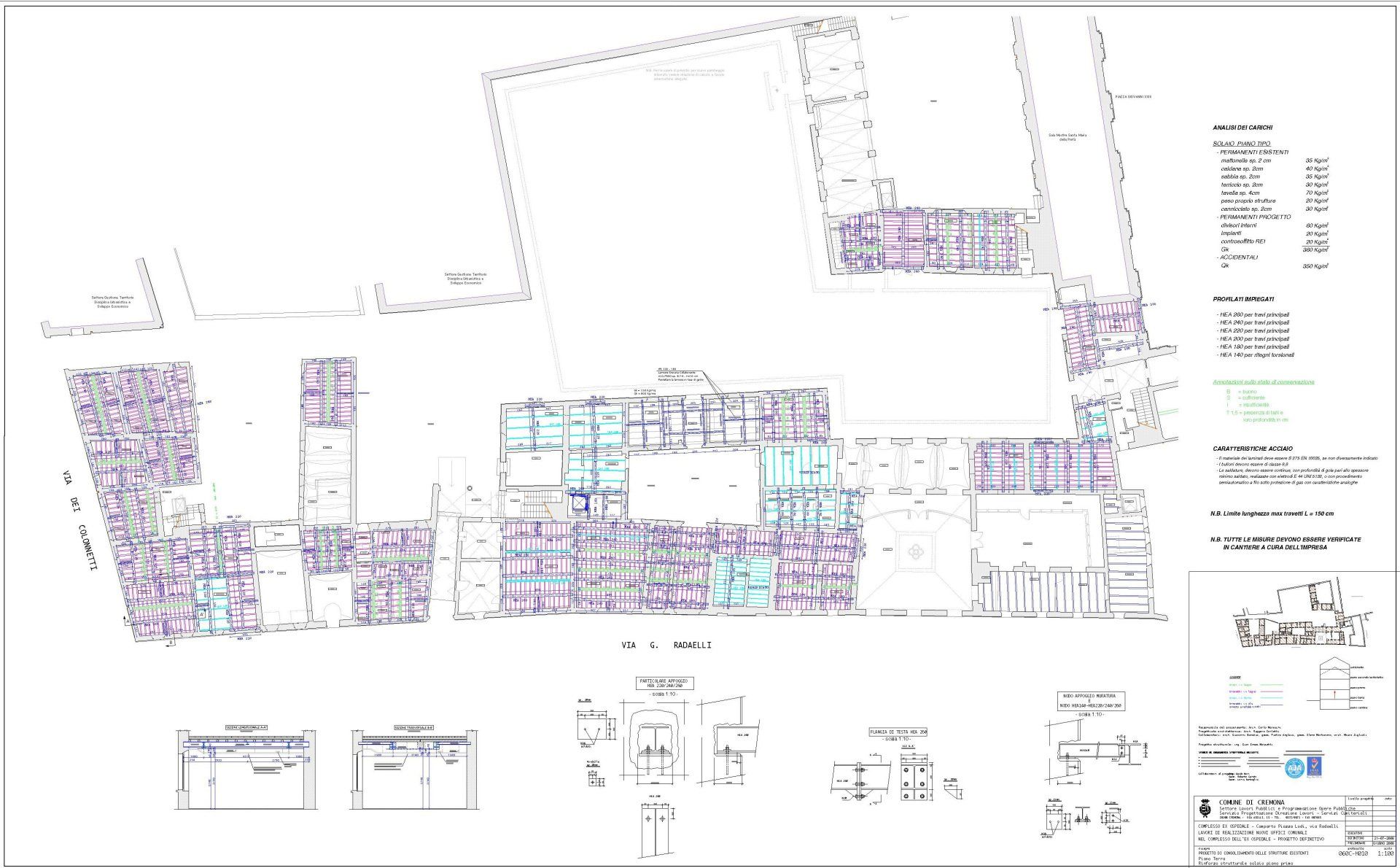
QF Palazzo Radaelli Cremona
QF Via Bissolati Cremona
State of degradation of Condominium Mirabello - Cremona
State of deterioration of Torretta CCIAA - Cremona
Apartment building in Via Palestro in Cremona
Cognitive investigations and monitoring
Cognitive investigations: a set of procedures and operations through which you have an overview of the state of the structure's conservation, quality of materials, cracking, and instability. This is useful for understanding the causes of failure and the best possible remedy.
Basilica of San Lorenzo in Cremona
Depending on the project, we can use:
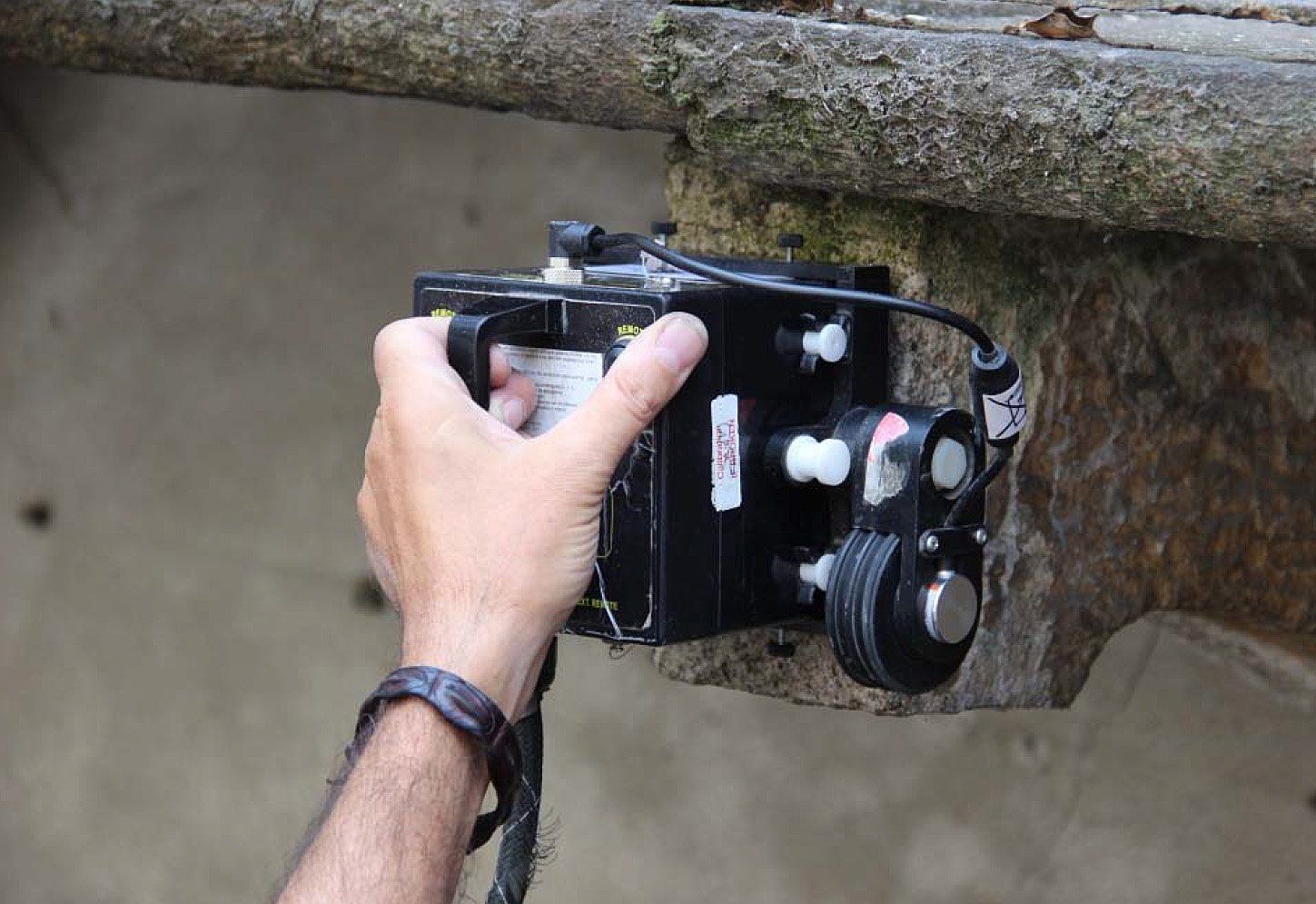
Sonic and ultrasonic
tests:
Non-Destructive Testing (PND) uses mechanical waves that originate from the elastic deformation of the element being investigated. The propagation speed of a material depends on its elastic modulus. Its response to stress and the frequency of these waves allow indirect analysis of its mechanical resistance. Mainly used for tests on concrete elements or masonry.
Sonic tests in San Bassiano
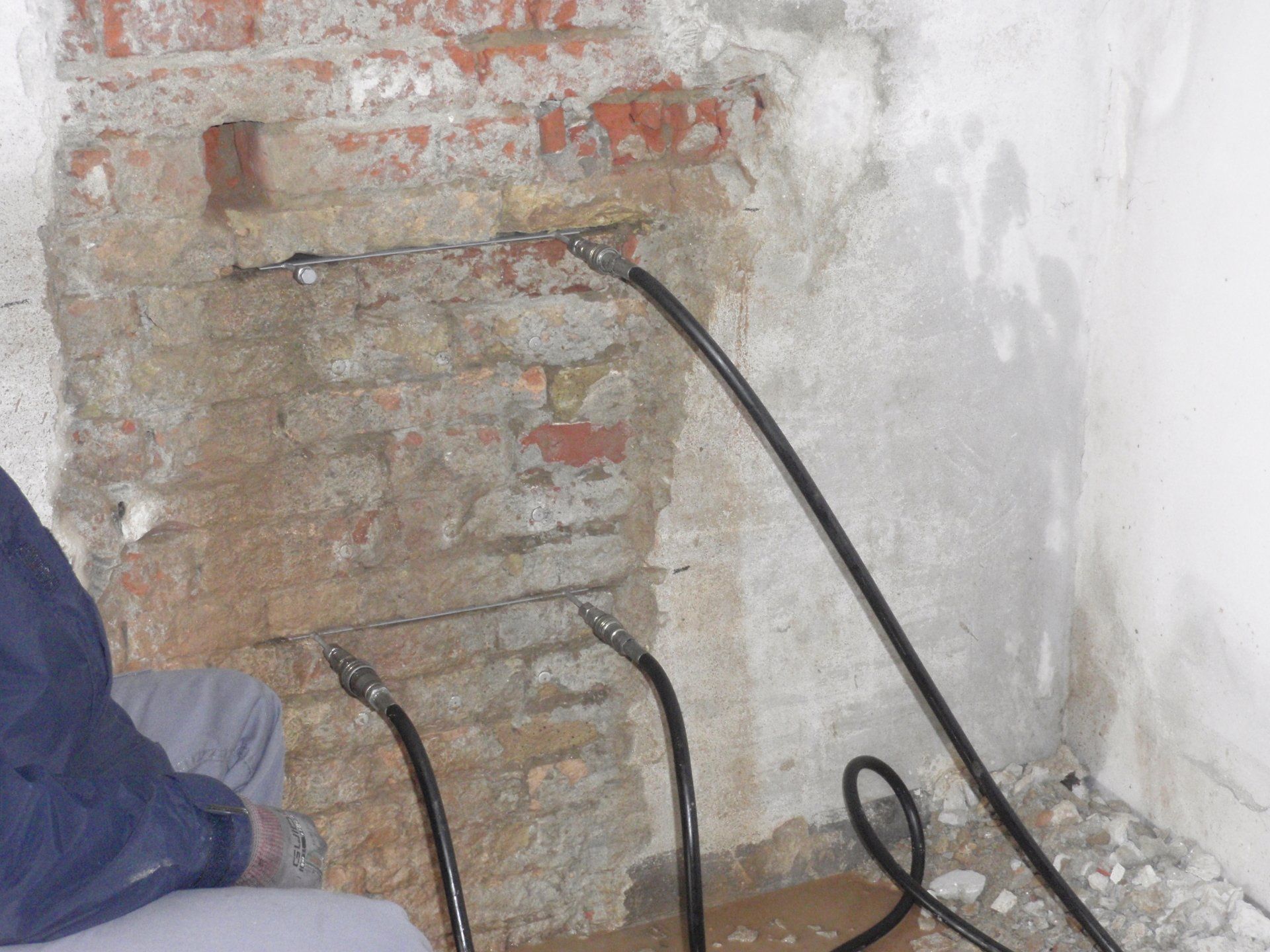
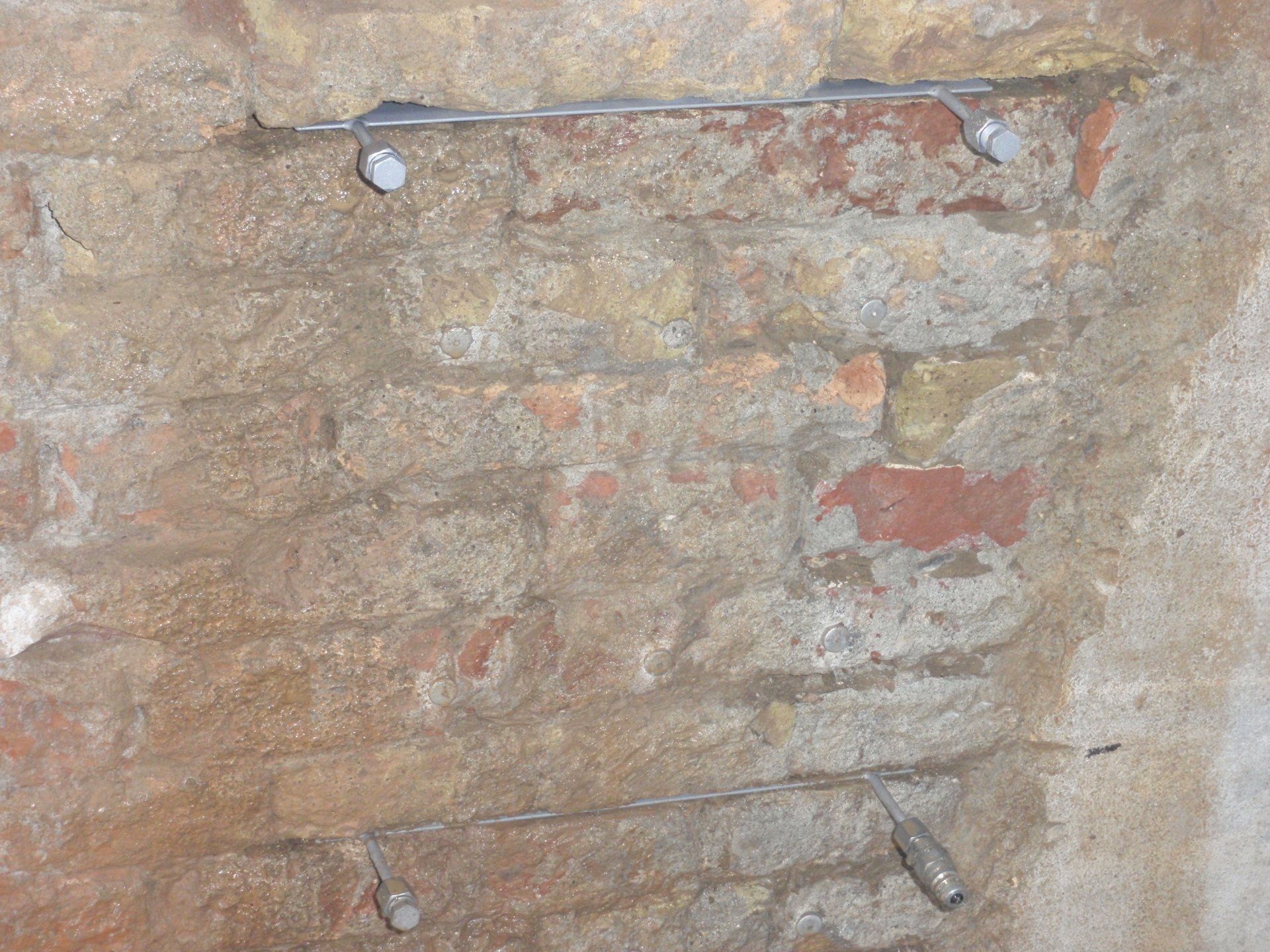
Flat jacks: these tests investigate the static conditions, the stress state, and the elastic modulus of a structure. For data acquisition, single flat jacks are used for determining the stress state, while two are used to determine the elastic modulus of the material.
Double cymbals in Vighizzolo CR02
Cutting tests: the direct cutting test is aimed at determining the average in-situ shear strength value of the masonry. The test consists of horizontally sliding machine into a brick element which is appropriately insulated from the rest of the masonry.
Cutting tests on brick Vighizzolo CR
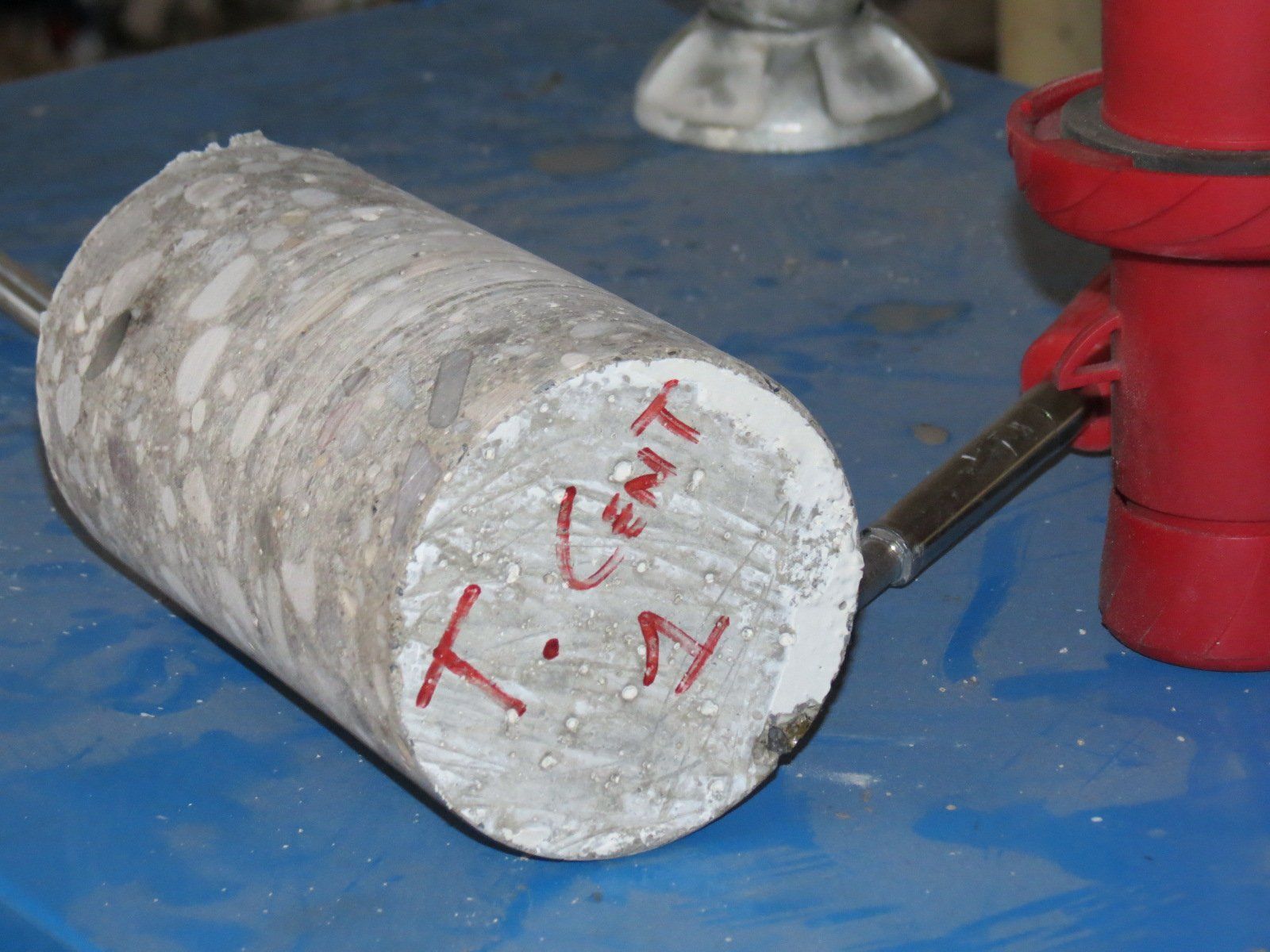
Core drilling: these are used to diagnose reinforced concrete buildings and structures. A destructive method, it determines the value of the compressive strength of the concrete conglomerate by means of compression tests. These are carried out in the laboratory on the "carrots" (cylindrical specimens), taken in situ using a coring machine.
Moglia capennone sampling tests
Sclerometric tests: non-destructive tests that are carried out with a sclerometer to determine the mechanical resistance of an element. This could be in concrete, masonry, or rock. They are applied directly to the element and the sclerometer reads the metal mass based upon its hardness.
SonReb (Sonic Rebound)
tests:
paired ultrasound tests and sclerometric tests.
Geo-radar tests:an electromagnetic method of investigation, these consist of a radar signal emitted by an antenna that penetrates the materials and reflects their electrical characteristics. This reflection is recorded, evaluated, and analysed. Signals are not recorded as waveforms, but colour coded.
Chain tension tests:
measures the pull to which chains are subjected, mainly for arcs or vaults. This method works with wood, iron, or steel, and has been used since ancient times. Hooks for the chains can be inserted during construction or in a subsequent phase of structural consolidation. These structural elements are bound to the walls by means of a key-cap, which can be single or double and are plate-shaped.
Pull-Out: a non-destructive extraction test which allows us to evaluate the quality of concrete structures and their compressive strength. Characterized by the insertion and then the subsequent extraction of blocks to evaluate the average compressive strength of the concrete. The insertion of the blocks can be done in two ways: when the concrete is still fresh or when it is already hardened. The maturing extraction involves the use of special machinery.
Pull-Off:
measurement of the tensile strength of concrete.
Thermographic test: a non-destructive test based on the analysis of infrared images of an element, detected using a thermal imager. Based on a study of the spectrum that is obtained, we can explain and describe the causes of the degradation of a building in relation to water and moisture infiltration, or we can search for hidden construction parts without requiring probing or demolition.
Laser scanner surveys: operations that use a set of sensors that communicate through a laser beam. This allows the detection of three-dimensional models of objects, buildings, or structures, as well as cracking. It can be used for internal geometric surveys of buildings, external shapes of facades, or to work out their verticality. Often used for monitoring structures, subsidence, and cracking over time.
Laser scan of San Gioacchino
Load tests: operations that verify the correspondence between theoretical data and actual data provided by an examination. This type of test can be carried out on horizontal elements, such as beams, shelves, and floors, or on inclined elements, such as pitched roofs or stairs.
The tests can be performed:
- with distributed loads using water tanks or ballasts;
- with concentrated loads, using hydraulic cylinders or hanging tanks.
Visual examinations: a set of checks that are carried out on a single structural part or on the entire work. Verifies degradation caused by atmospheric agents, infiltration of water, damage caused by stresses or movements of the structure, changes to the initial framework, and the development of cracks and fissures. In some cases, this is summarized using testimonials, which list and describe what has been found, room by room with rich details, photos, and schematic plans. Once completed and signed by all the parties involved, the documents can be sworn in court.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is the synthesis of systematic studies into the causes and effects of changes to a structure, derived from a series of monitoring surveys conducted over time (and dependent on the type of structure to be analysed).
"Nature is the source of all true knowledge. She has her own logic, her own laws,
she has no effect without cause nor invention without necessity"
LEONARDO DA VINCI - Thoughts
Remedies and consolidation
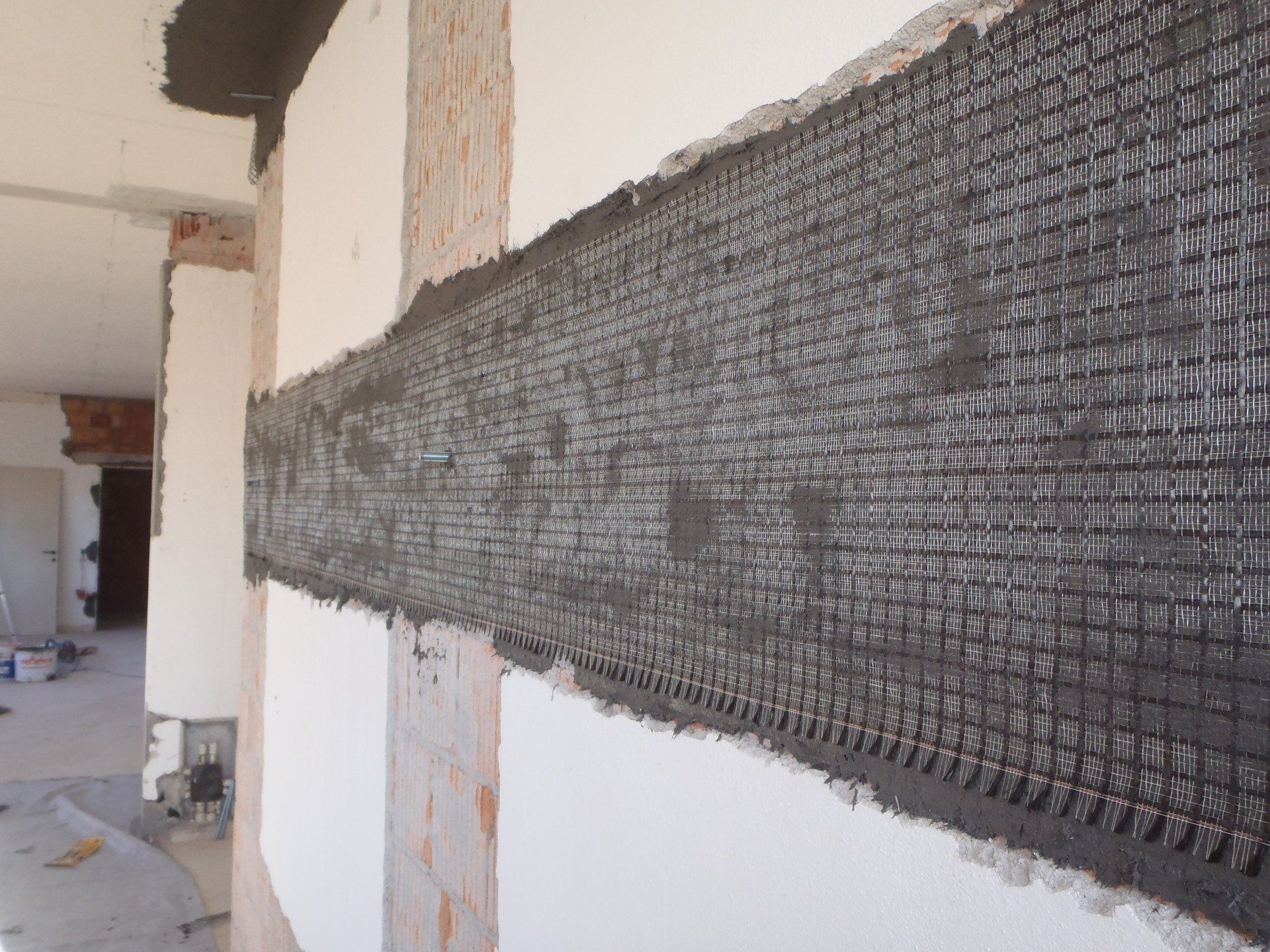
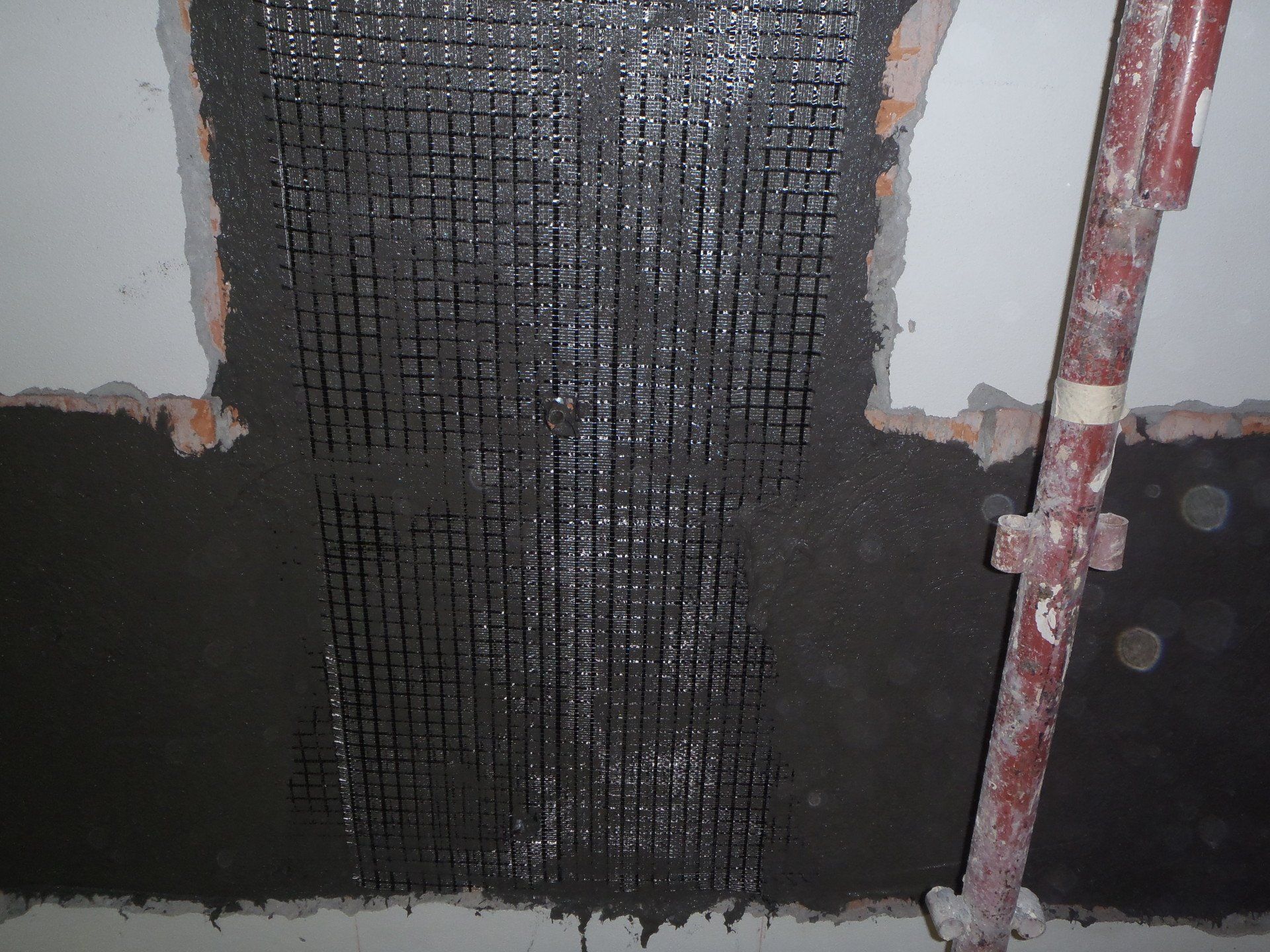
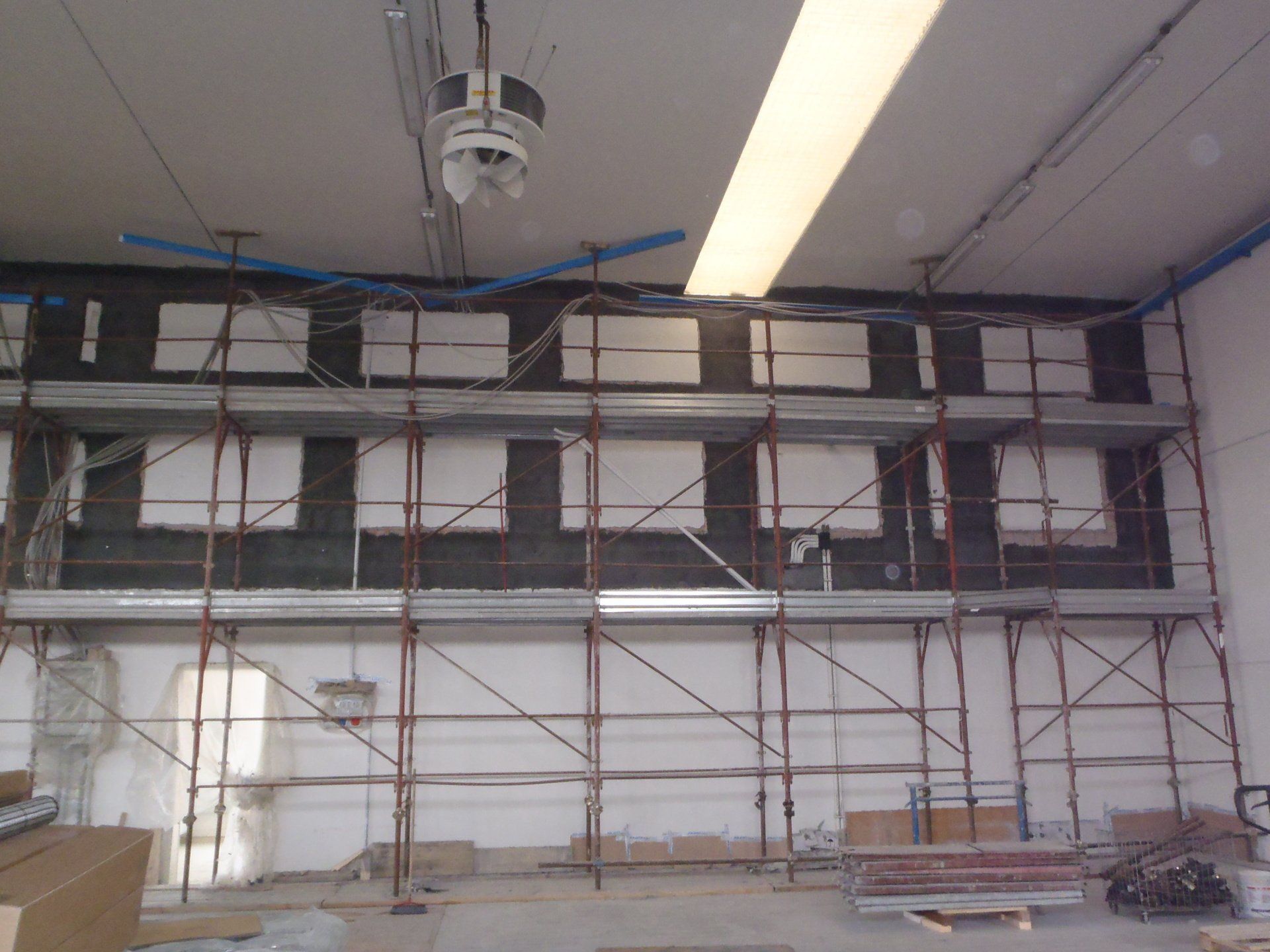
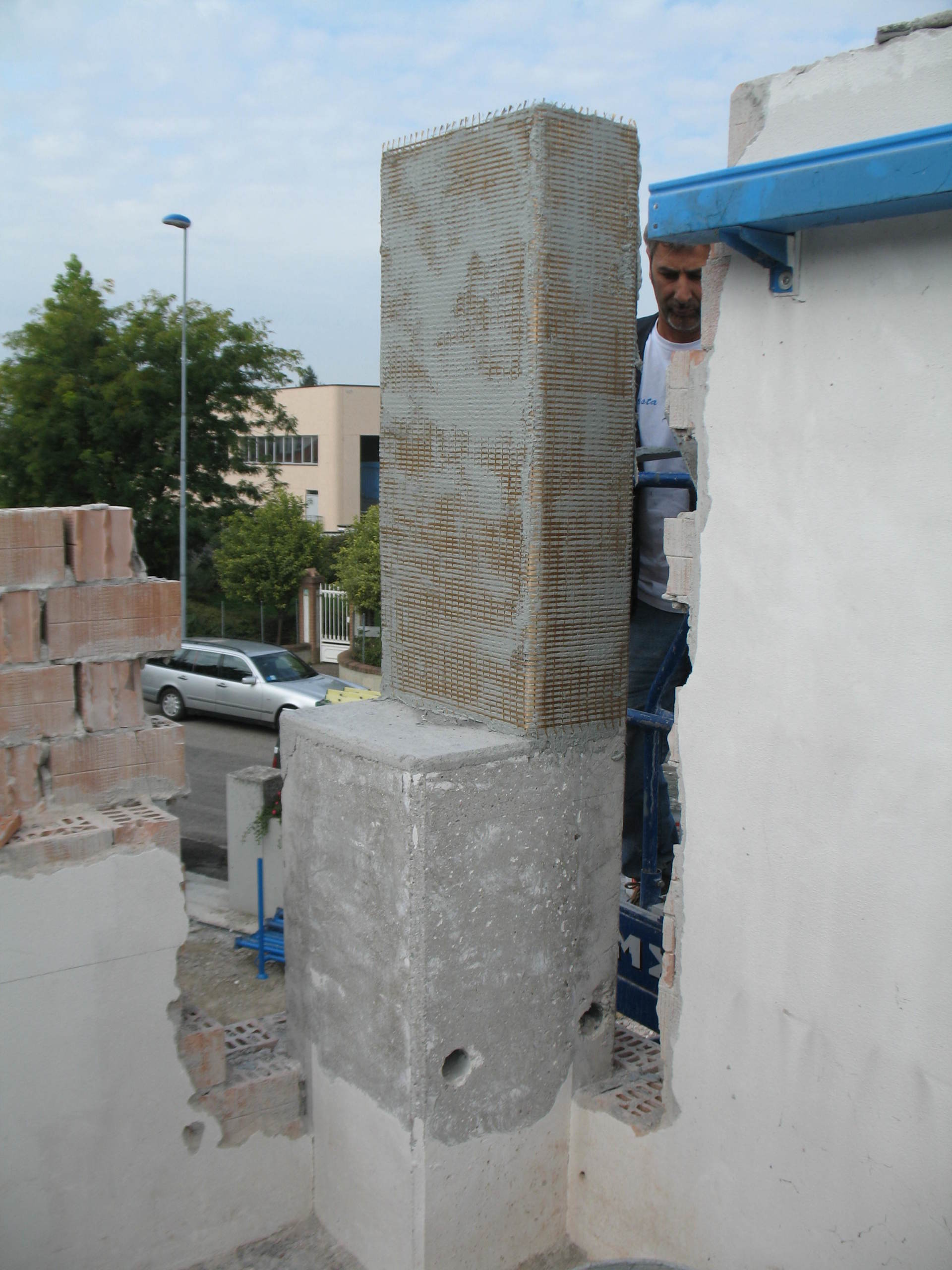
Remedies: possible solutions to the causes of deterioration and to the crack pattern that has occurred. Depending on the type of intervention, there may be more or less invasive remedies (injections of mortar or resins, scuci sewings, demolitions/reconstructions, PBO fibres, FRCM, etc).
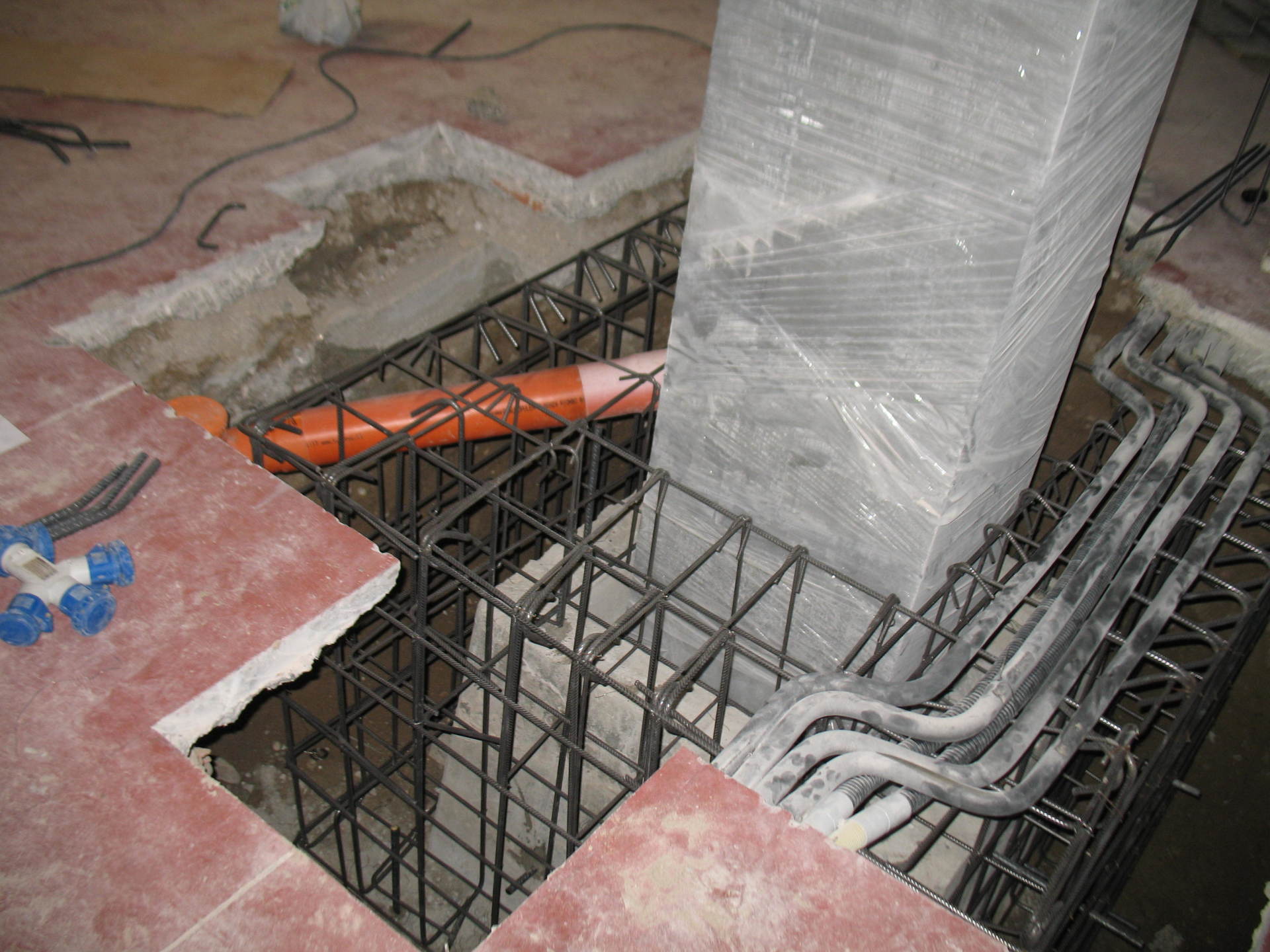
Interventions on reinforced concrete elements
Post-earthquake intervention - Capannoni in Moglia - MN
Interventions with fibres
Post-earthquake intervention - Moglia - MN
Interventions with fibres
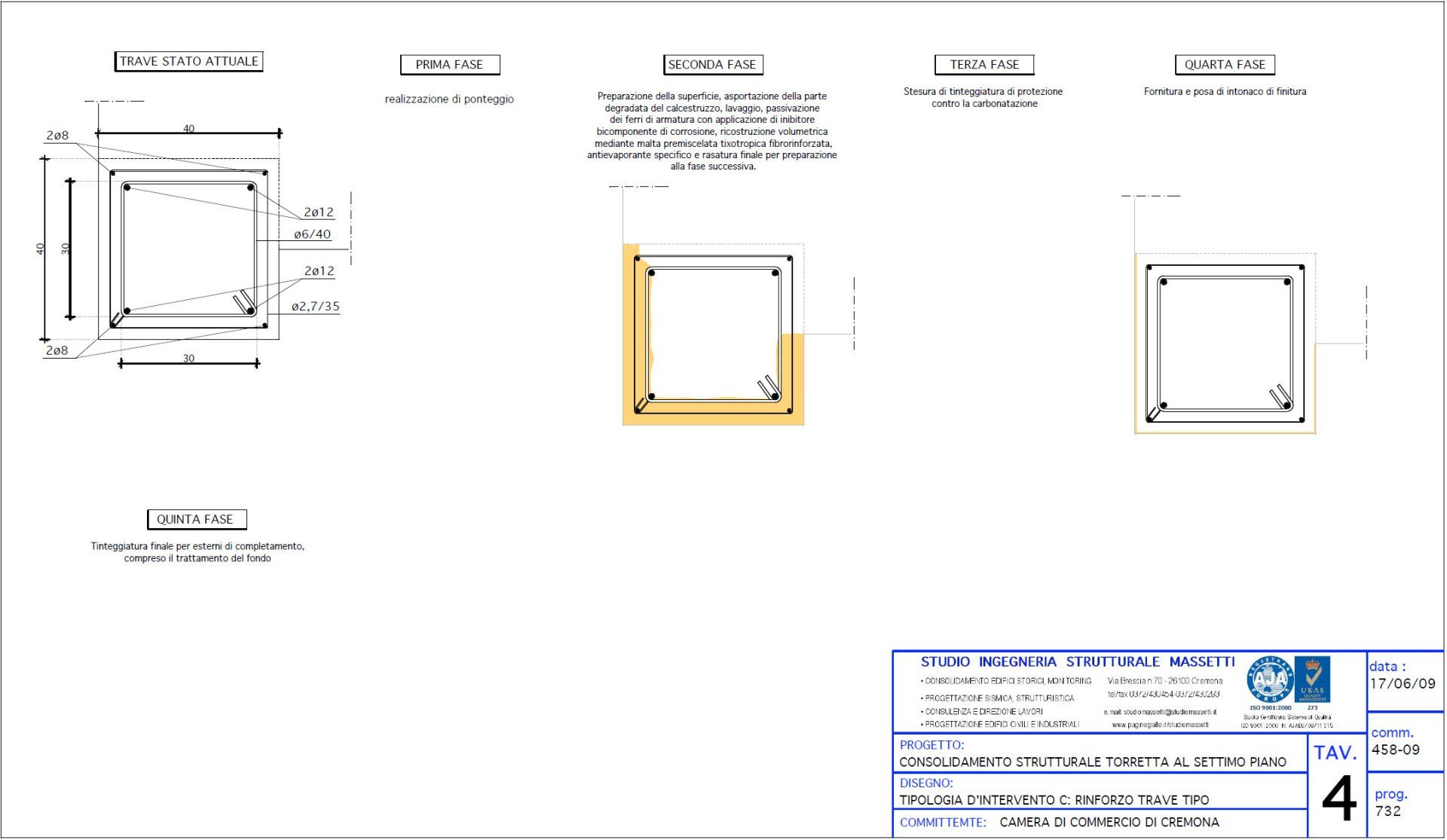
Cremona CCIA Tower
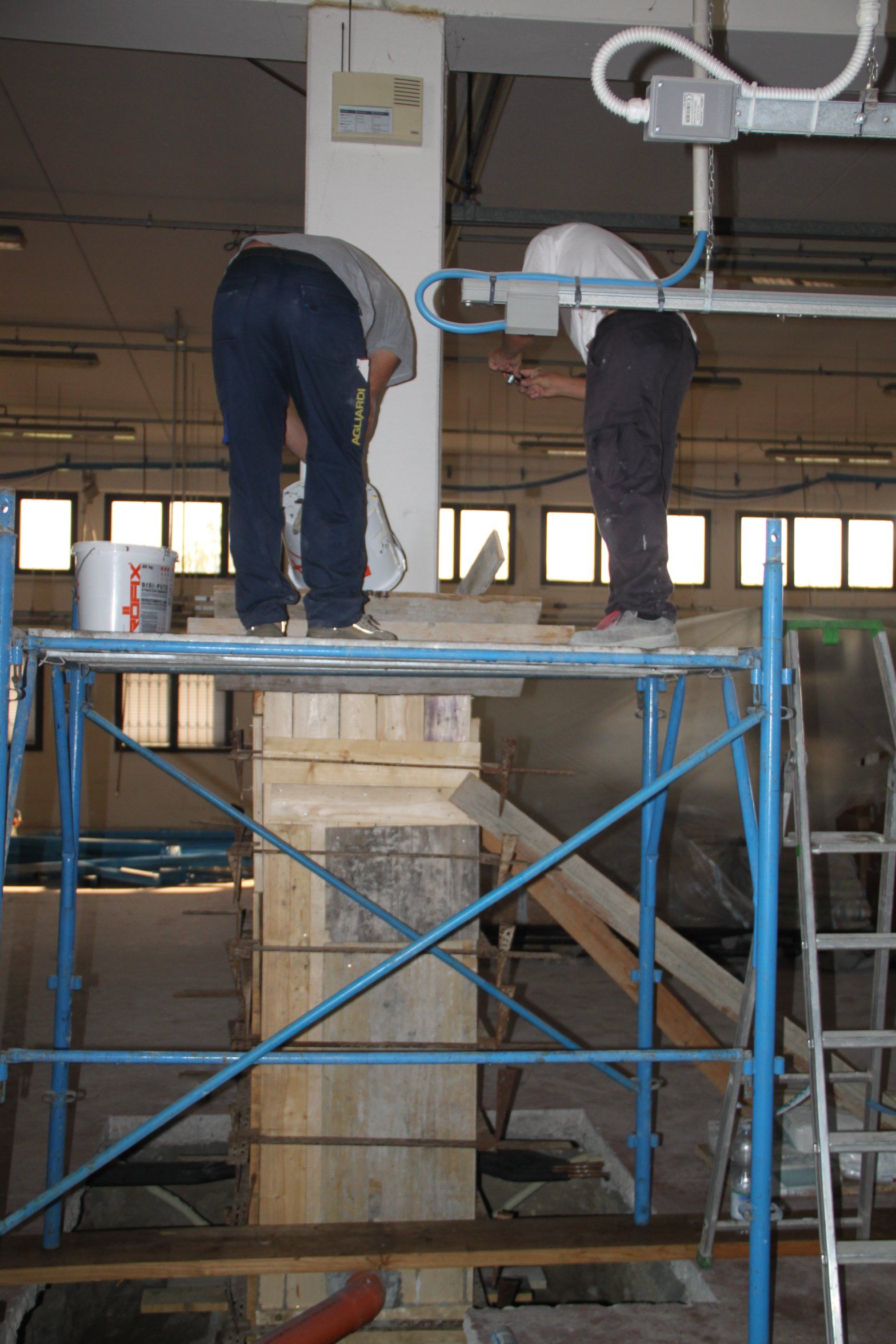
Interventions on the walls
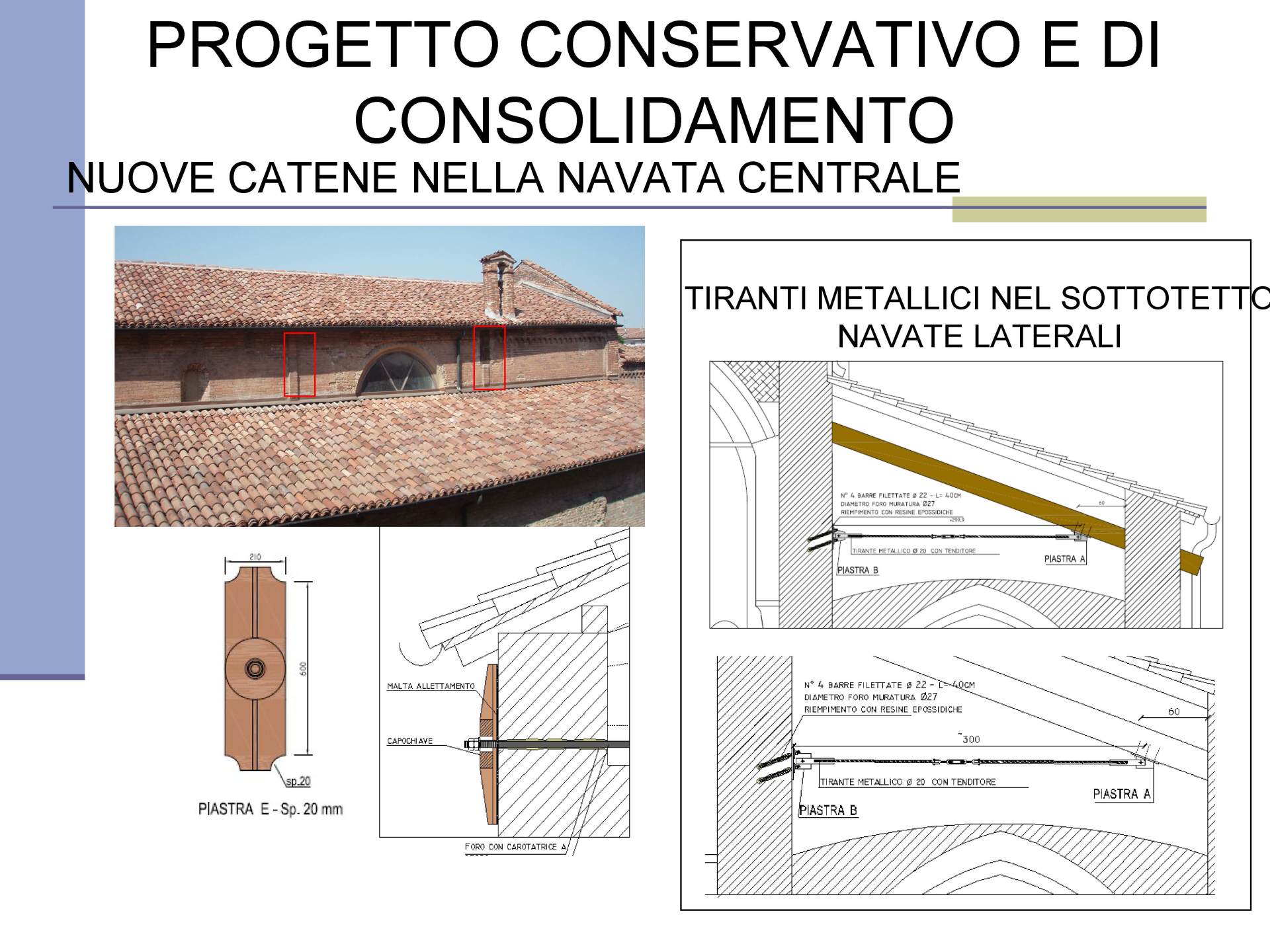
San Gioacchino - Bosco ex Parmigiano
Interventions on the walls
Basilica of San Lorenzo in Cremona
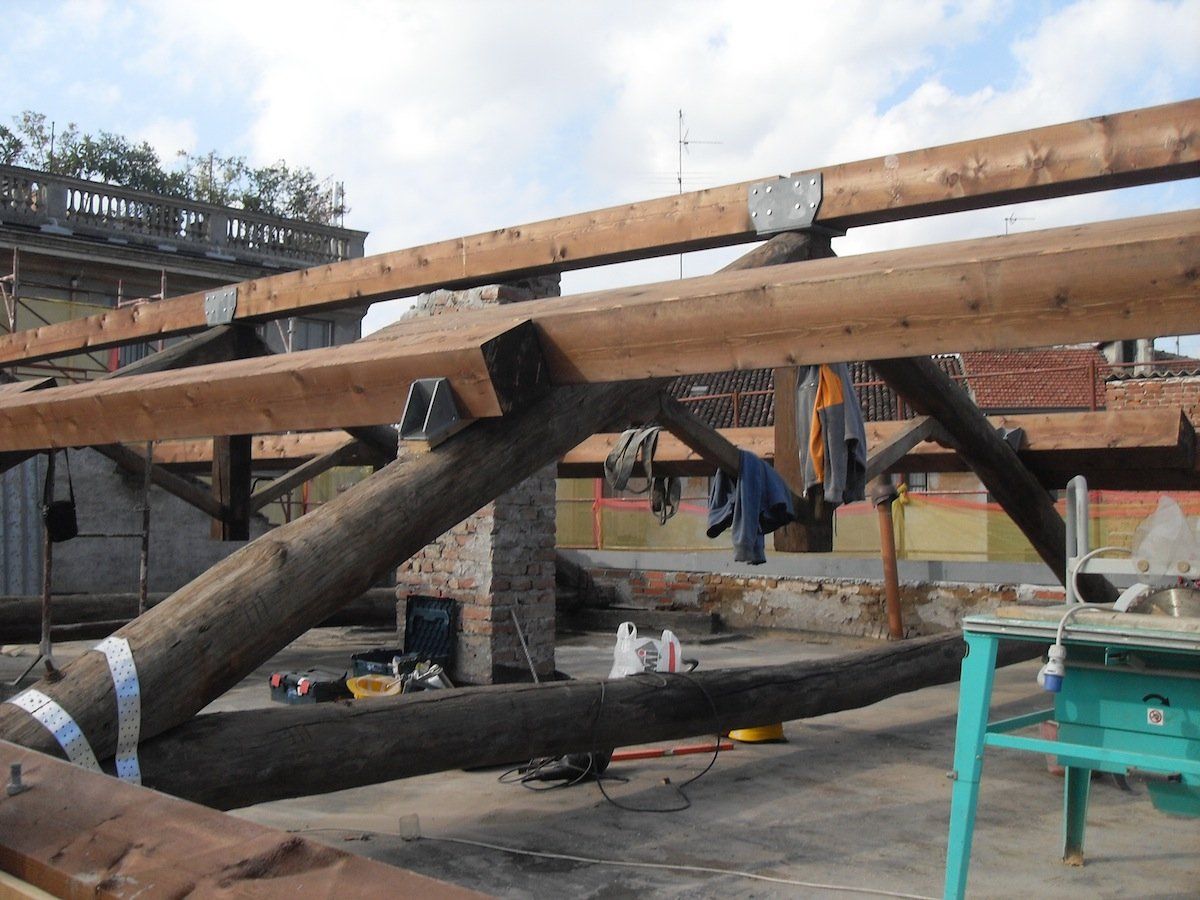
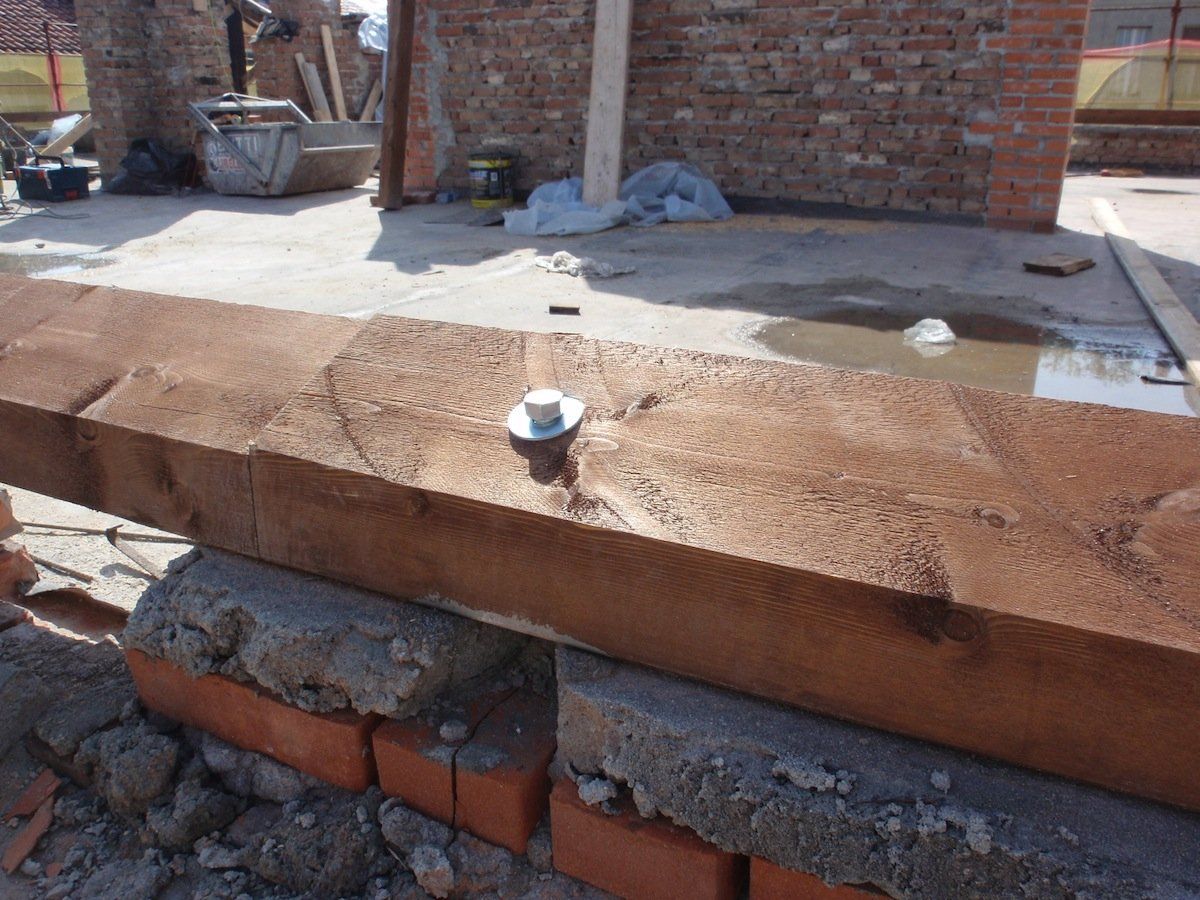
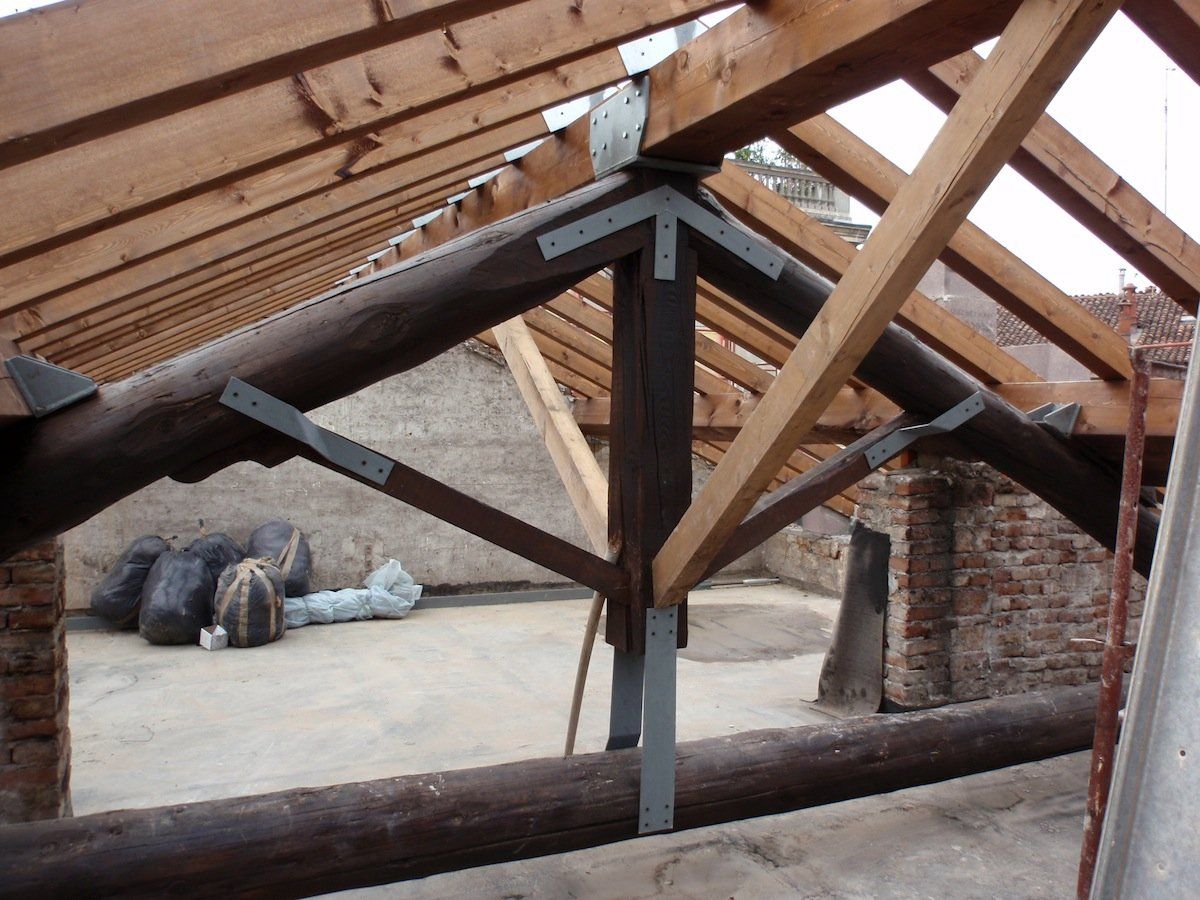
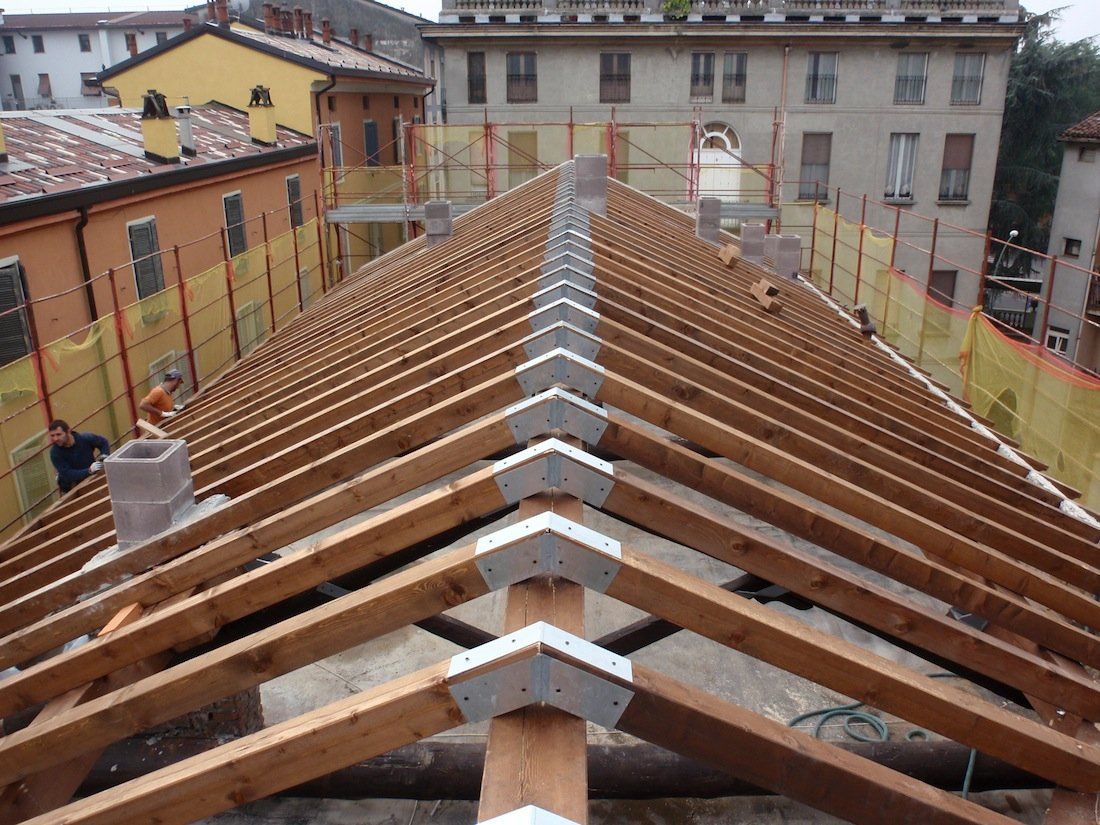
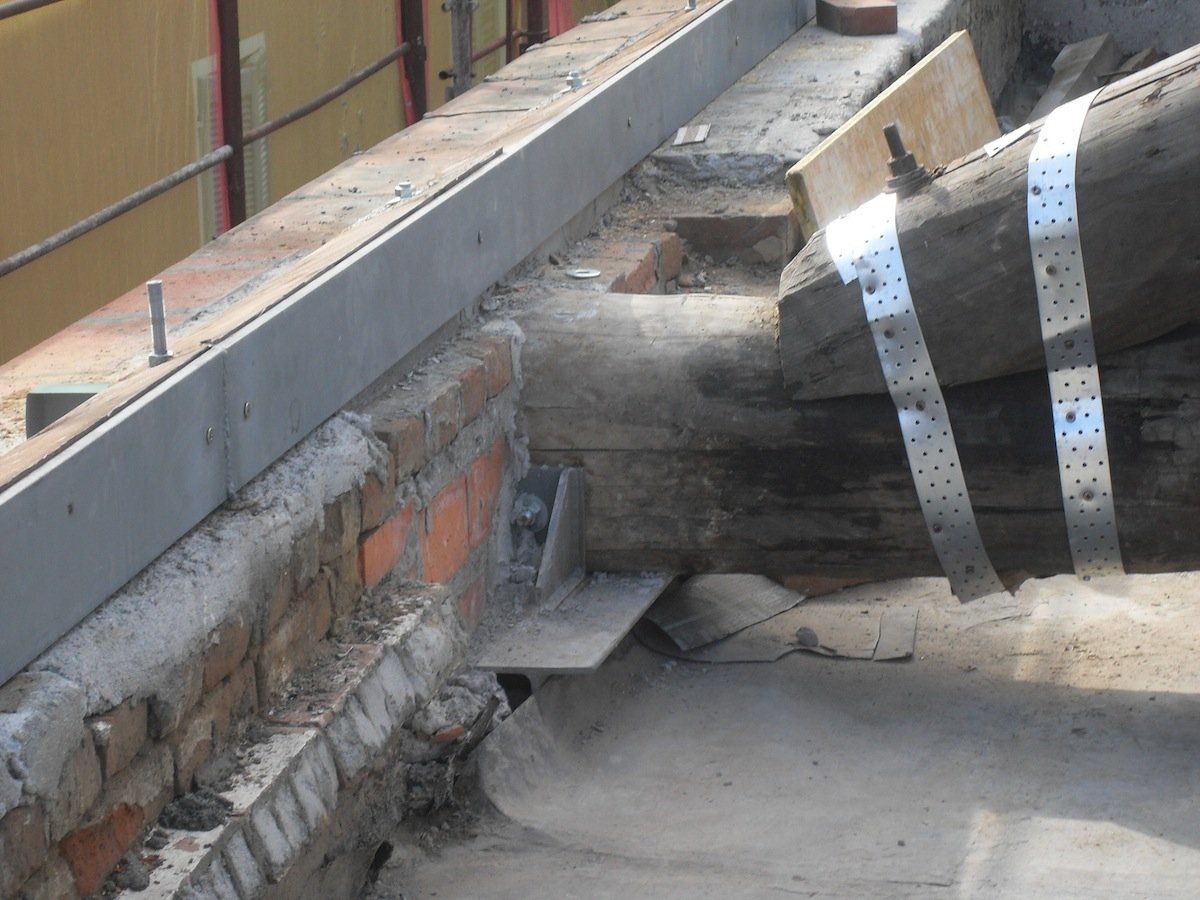
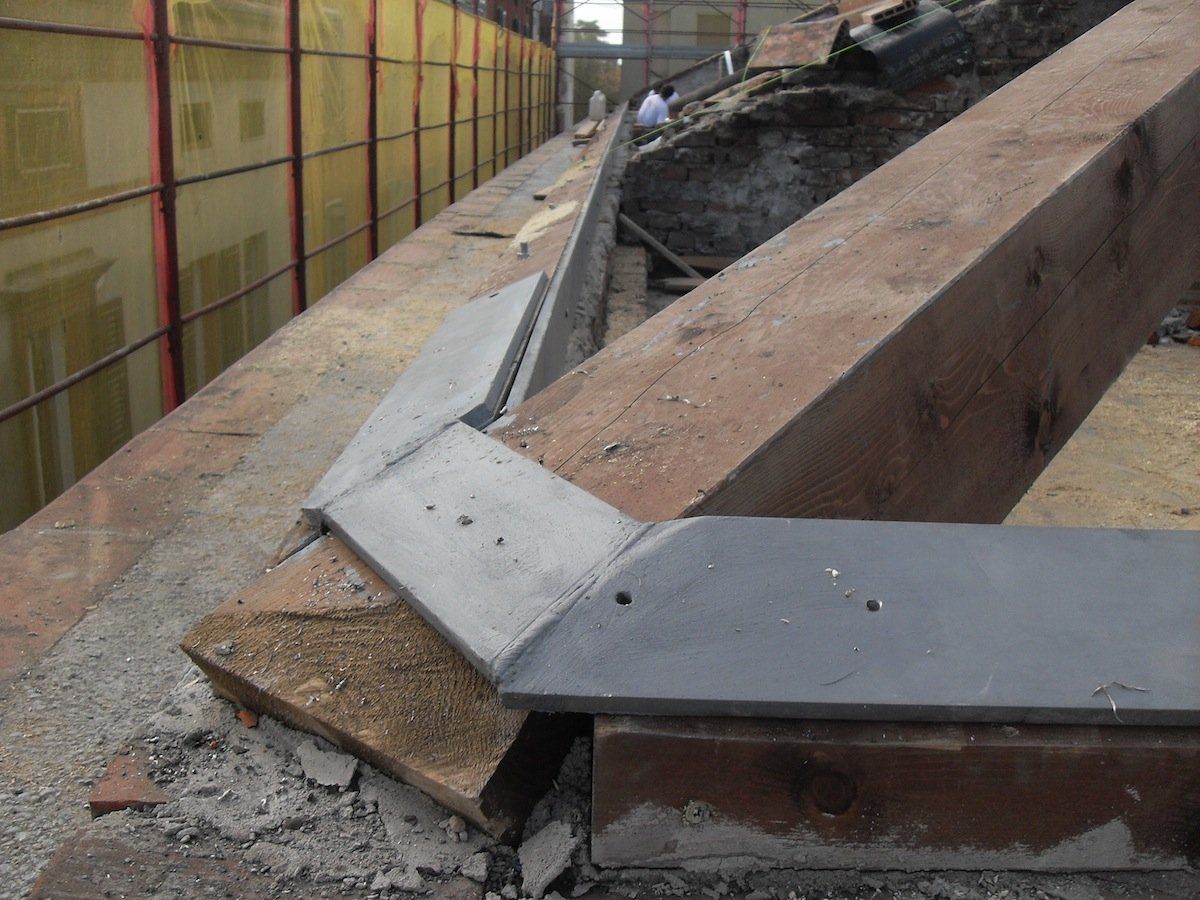
Interventions on wooden elements
Apartment building Via Dante 63 Cremona
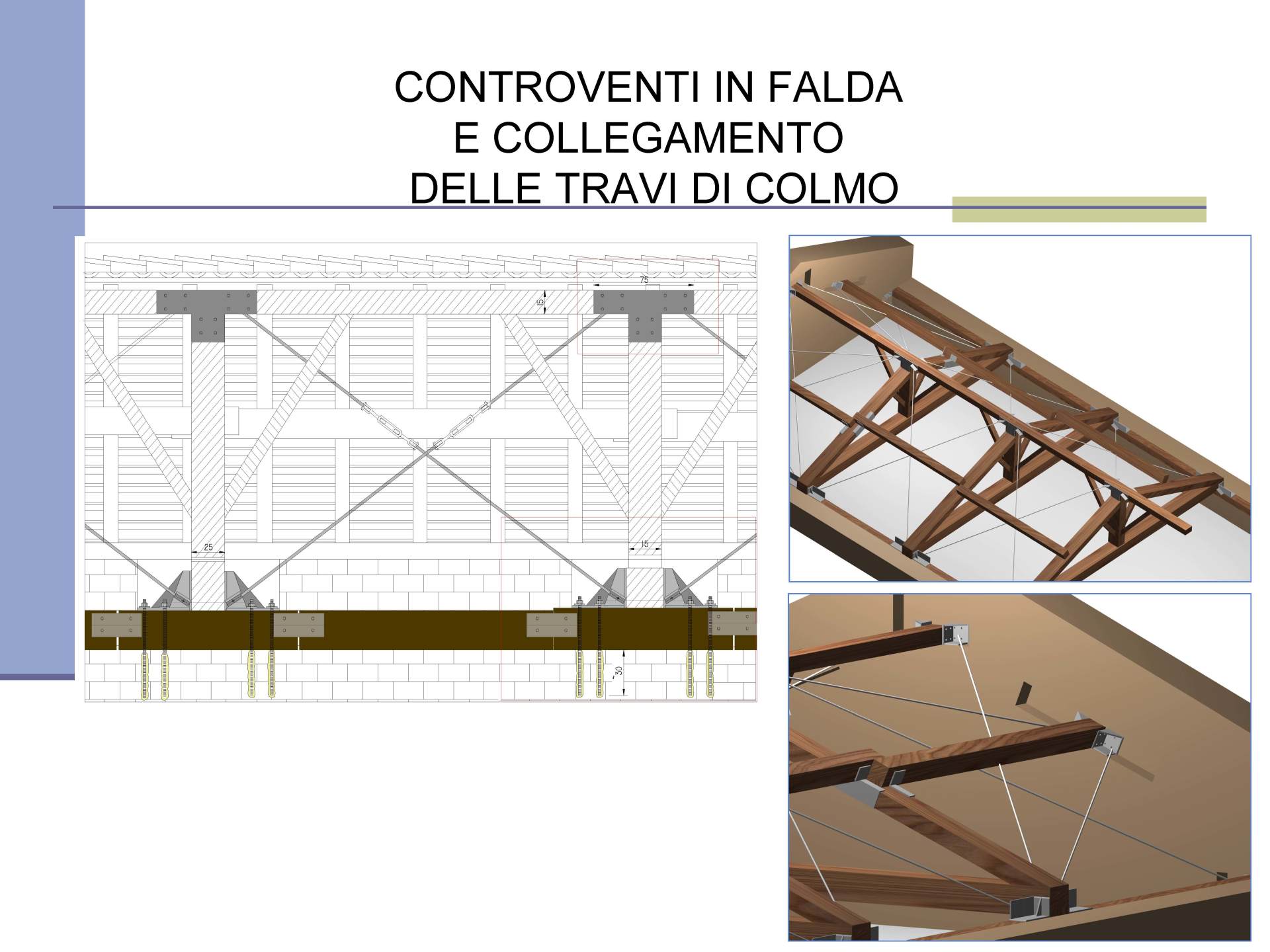
Interventions on wooden elements
Basilica of San Lorenzo in Cremona
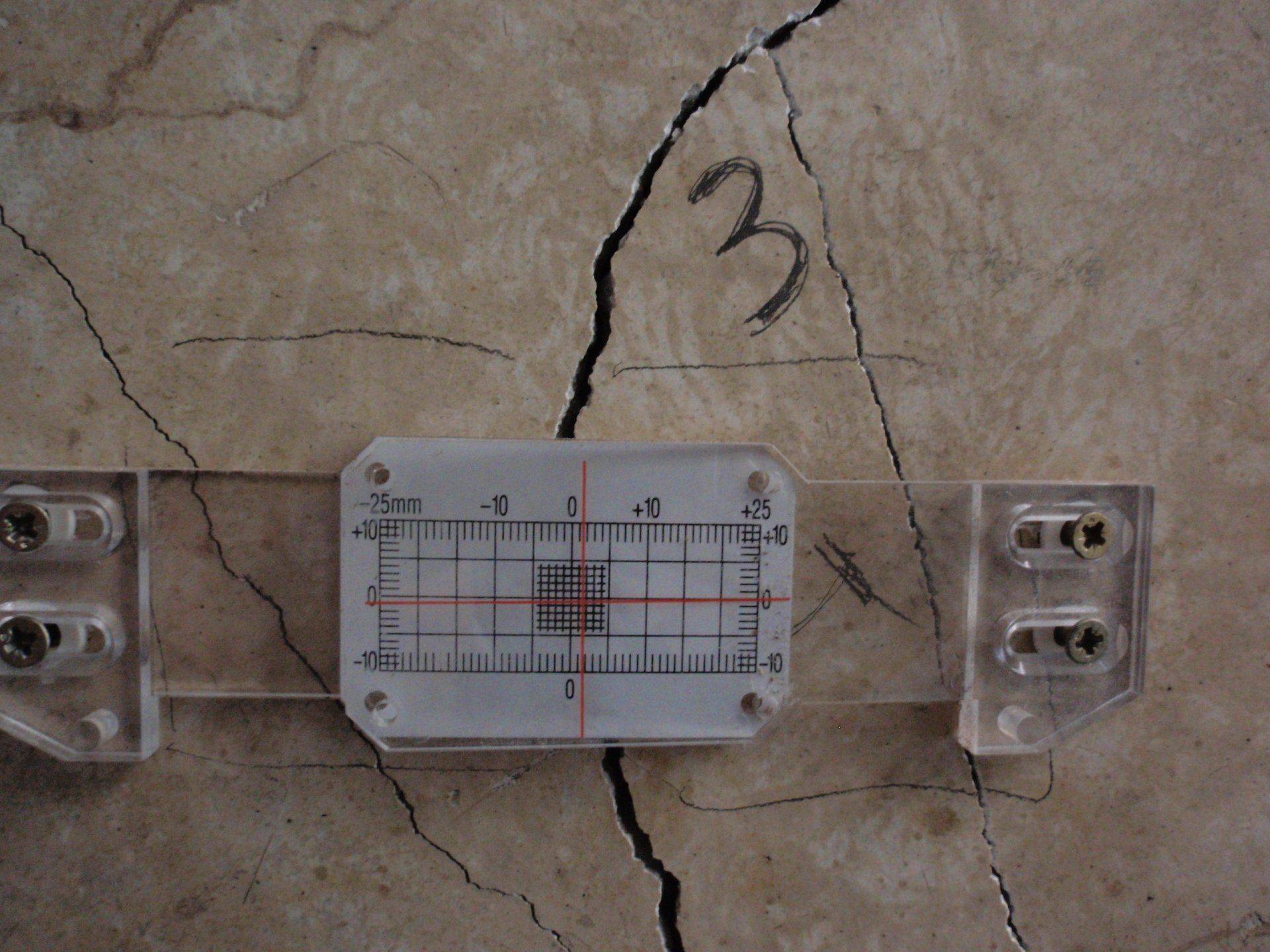
In progress or post-intervention monitoring
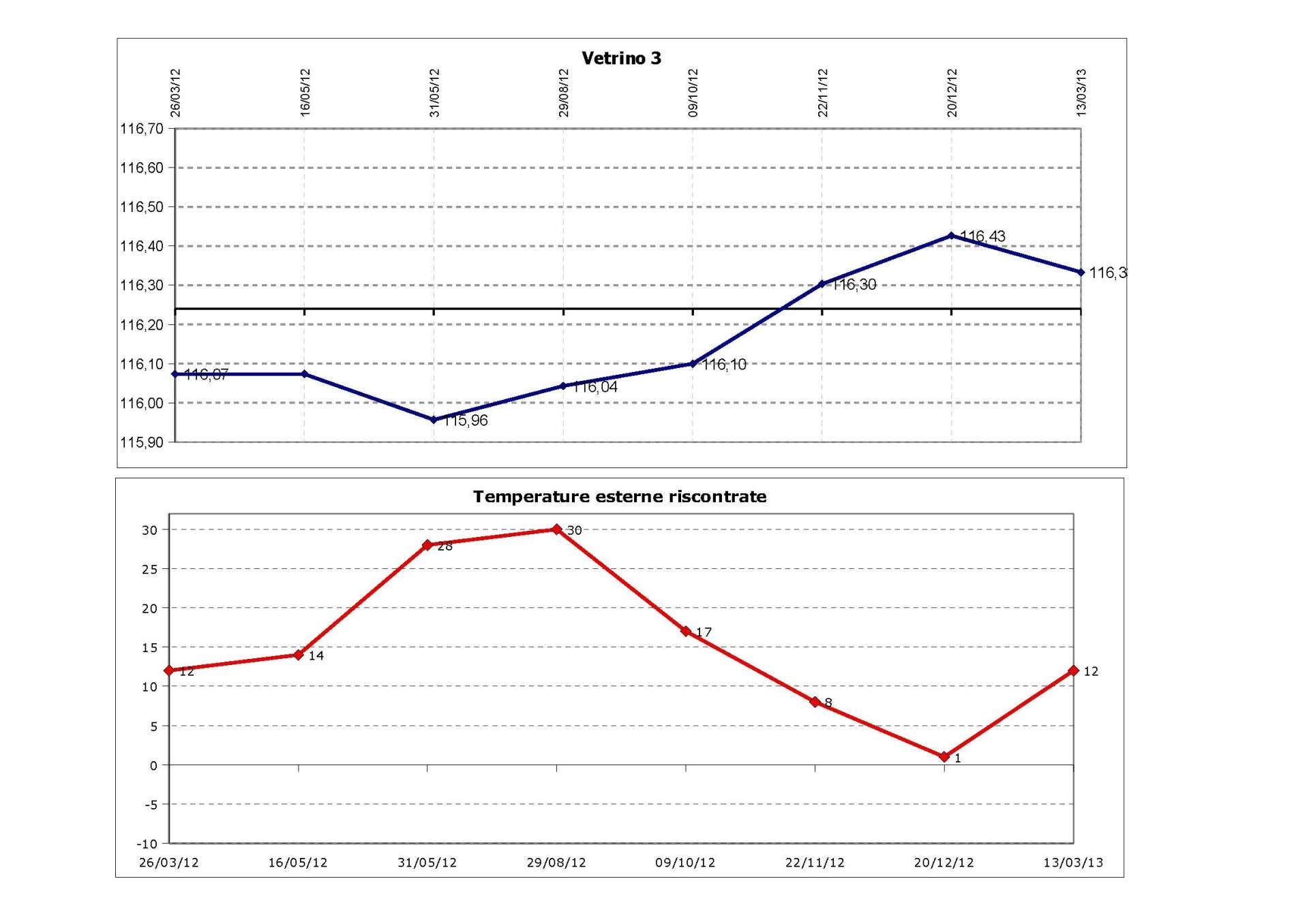
This is carried out in the next phase of an intervention, monitoring the correct execution of the work over time and checking that there are no subsequent movements or new damage.
Injury monitoring